Stamens 10–30, basically 2 opposite to and 2 alternating with each corolla lobe, but there are many modifications of this arrangement; anthers slightly exserted or at least clearly visible at the throat, lanceolate or narrowly oblong, usually strigulose, often dehiscing at first by large ellipsoidal apical pores which later become longitudinal slits; filaments usually shorter than the anthers.
Seed subglobose, with 3 radiating lines from the apex; embryo with cotyledons flexed at right–angles to the radicle; radicle entirely surrounded by an invagination of the testa.
Ovary globose, hairy or covered with peltate scales, locules usually 4–6 and uniovulate, occasionally 2–3 and incompletely septate and biovulate.
Styles 2–3, free or united in lower half, often as long as ovary, usually glabrous, ending in a slightly expanded bilobed stigmatic surface.
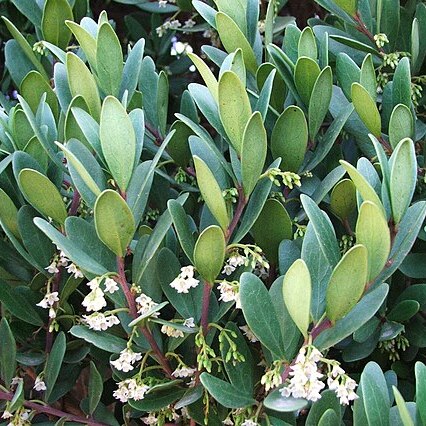
Leaves alternate, subopposite or siibverticillate, coriaceous, margin sometimes crenulate, otherwise entire.
Inflorescence a simple or branched false raceme, or rarely (not in our area) flowers solitary.
Fruit a small, globose, 1 (3)–seeded berry up to 1 cm. diameter; mesocarp exiguous.
Calyx 4–5–lobed shallowly cyathiform or patelliform, not accrescent.
Corolla campanulate, 4–5–lobed, usually to beyond the middle.
Flowers dioecious, the male usually larger than the female.
Pistillode usually very reduced, with or without stylodes.
Trees, shrubs or suffrutices, usually evergreen.
Disk fleshy, fimbriate, sometimes undulate.
Staminodes absent or very reduced.