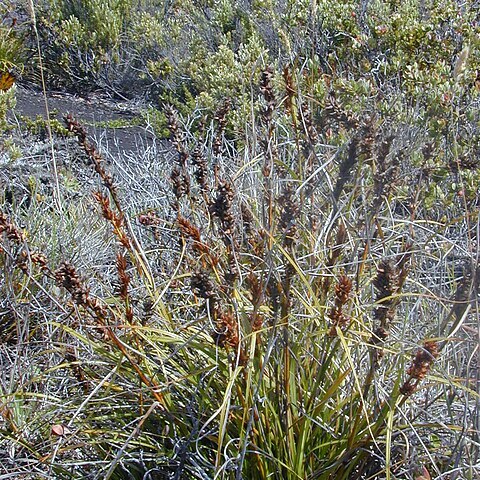
Perennials with short, woody, descending rhizome, often forming large tussocks. Stolons absent. Stems erect, usually tall and stout, terete, multistriate, usually few-noded, many-leaved at the base. Basal leaves crowded, cauline ones spirally arranged, narrowed above the base, often scabrous on the margins, inroiled, narrowed into a long subulate point; ligule well developed. Inflorescence paniculate, consisting of several fascicles of secondary panicles, usually long and loose; bracts similar to the leaves, the upper ones gradually shorter; branches and branchlets never anfractuose; tubular prophylls (cladoprophylls) absent. Spikelets numerous, solitary or 2-4 together, brown or black. Flowers 1 or 2, the upper one bisexual, fertile, the lower one when present sterile or ♂, usually very precocious. Glumes spirally arranged, outer ones lanceolate, acuminate, keeled, scabrous on back and margins, inner ones small, delicate in anthesis, in fruit elongated, hard, concave, obtuse, tightly enclasping the flower(s). Hypogynous bristles absent (except in 2 extra-Malesian spp). Stamens (2-)3-6; filaments often lengthening after anthesis, persistent at the base of the nut (see Note); anthers with produced connective. Style (2-)3-fid, sometimes 4-fid (due to one of the branches being bifid); Style-base small, not swollen, adnate to the nut. Nut ovoid or ellipsoid, terete, trigonous, or obscurely 4-angled, shining; endocarp thick, hard, the inner side annulate-sulcate by 5-10 transverse grooves, or smooth.
Herbs, perennial, forming slender to massive tussocks. Roots stout. Rhizomes woody. Culms erect, usually tall and robust, terete, several noded. Leaves linear, deeply many channeled, narrowly crescent-shaped, twisted lengthwise through 180°, involute on drying; ligule present, usually truncate, papery. Inflorescences plumose-paniculate, usually decompound, consisting of several fascicles per node. Spikelets brown or black, numerous, solitary or 2-4 together. Flowers 1 or 2, apical one bisexual, usually with a second more basal one male. Glumes black or dark brown, spirally arranged, papery; basal 3-8 glumes empty, lanceolate, keeled, abaxial surface and margin scabrous, apex acute; apical 2 or 3 glumes smaller than remaining ones, thin at anthesis but becoming thick in fruit, apex obtuse; apicalmost glume bearing a bisexual flower. Perianth bristles absent. Stamens (2 or)3[or 6]; filaments elongating markedly after anthesis, persistent on nutlet and entangled in glumes thereby suspending fruit. Stigmas 3[or 4]. Nutlet ovoid, ellipsoid, obovoid-fusiform, or globose, terete or 3-sided; endocarp blackish, thick, bony.