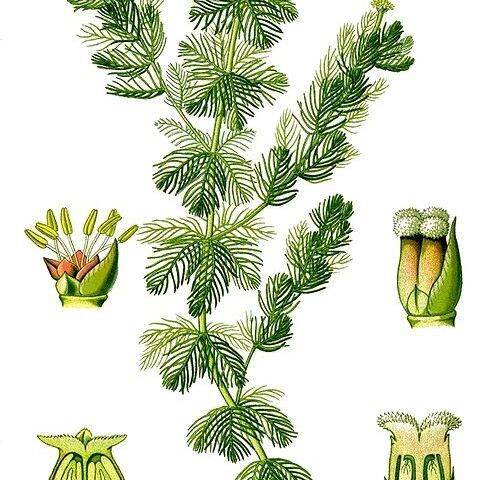
Fruit a nutlet or drupe, bluntly angular, ribbed or winged with 1–4 1-seeded locules or divided in 2 or 4 1-seeded cocci. Seeds with abundant fleshy albumen. Aquatic or terrestrial herbs or subshrubs with hermaphrodite, monoecious or dioecious flowers. Leaves usually exstipulate, alternate, opposite, whorled or all radical, sometimes very small, the blades simple, entire or ± divided especially in the case of submerged leaves. Inflorescences axillary or terminal, the flowers in cymes, fascicles, racemes, panicles, spikes or solitary; bracts often present. Flowers often bracteolate, usually small, regular. Calyx with the tube adnate to the ovary; lobes 2–4, valvate, sometimes rudimentary or absent. Petals 2(–3)–4, valvate or slightly imbricate-contorted, or sometimes absent. Stems (1–)2–8; filaments long or short; anthers basifixed, 2-thecous, dehiscing by lateral slits. Ovary inferior, rounded or angular to winged, 1–4-locular; locules 1-ovulate; ovule apical, pendulous, anatropous; styles 1–4, free or absent; stigmas papillate or plumose
Plants ephemeral, annual or perennial, herbs, subshrubs, shrubs or rarely small trees, monoecious or dioecious. Leaves simple, opposite, alternate or whorled, exstipulate, entire to pectinate. Inflorescence usually a spike-like, or simple or of compound dichasia, sometimes compressed into a globular or flat-topped corymb; each flower or dichasium subtended by a pair of bracteoles. Flowers bisexual or unisexual, actinomorphic, 4-merous, rarely 3-or 2-merous. Sepals usually 4. Petals usually 4, usually hooded or navicular. Stamens usually 8, rarely 4; anthers ovoid to linear, 4-locular, basifixed, sometimes apiculate; filaments usually elongating after anthesis. Ovary inferior, usually completely or incompletely 4-locular; ovules pendulous, 1 or 2 per locule (if 2, then 1 aborts); styles usually 4, free; stigmas usually capitate, fimbriate. Fruit an indehiscent nut or schizocarp splitting into 4 mericarps, 1–4-locular, variously winged or ornamented. Seeds 1 per locule.
Herbs or undershrubs, often aquatic; leaves alternate, opposite or verticillate, sometimes very large, the submersed ones often much divided; stipules absent
Inflorescences axillary or terminal, the flowers usually small, arranged in cymes, fascicles, racemes, panicles or spikes, or solitary; bracts often present
Leaves alternate, opposite or verticillate, pinnately or palmately nerved, sometimes very large, the submerged ones often much divided; stipules absent
Gynoecium 1–4-locular; ovules 1 in each loculus, pendulous from the apex; styles 1–4 or absent; stigmas papillose or plumose
Stamens 2, 3, 4 or 8, rarely 1 or absent; anthers basifixed, 2-celled, dehiscing lengthwise; filaments mostly filiform
Ovary inferior, 1–4-celled; styles 1–4; ovules as many as the styles, pendulous from the apex of the cells
Calyx-tube short, adnate to the ovary; calyx-lobes 2–4, mostly valvate and persistent, or absent
Fruit small, a nut or drupe, sometimes winged, indehiscent or rarely breaking up into cocci
Fruit a nutlet, indehiscent or breaking up into 2 or 4 single-seeded mericarps, or a drupe
Flowers hermaphrodite or unisexual, solitary to paniculate or corymbose, often very small
Seeds pendulous, with copious endosperm and straight fairly large (rarely small) embryo
Stamens 2–8, rarely 1, large; anther basifixed, 2-celled, opening lengthwise
Herbs or undershrubs, often aquatic, monoecious, polygamous or dioecious
Petals 3–4 or absent, valvate or slightly imbricate
Calyx-tube adnate to the ovary; lobes 2–4 or absent
Petals 2–4, valvate or ± imbricate, or absent
Seeds with abundant fleshy or oily endosperm