Herbs or small shrubs, prostrate or erect; stems mostly angular by the decurrent edges of the petiole. Leaves (in Mal.) simple, decussate or in whorls of 3-4, rarely alternate, pinnately nerved, the margin almost always dentate, serrate, or crenate. Inflorescences terminal. Flowers (in Mal.) solitary in the axil of a bract, bisexual, (in Mal.) 4-merous. Sepals (in Mal.) 4, valvate in bud, mostly triangular, persistent. Petals (in Mal.) 4, imbricate in bud, boat-shaped, caducous. Stamens (in Mal.) 8, rarely 4, in the latter case episepalous (in one extra-Mal. sp. epipetalous). Ovary (in Mal.) often 4-gonous, 8-ribbed, the mid-sepaline ribs less distinctly raised than the others, 4-celled; pericarp enlarging to fruit-size long before the seed is set; styles (in Mal.) 4, cylindric, often incurved or the stigmas sessile. Fruit nut-like, pericarp hard.
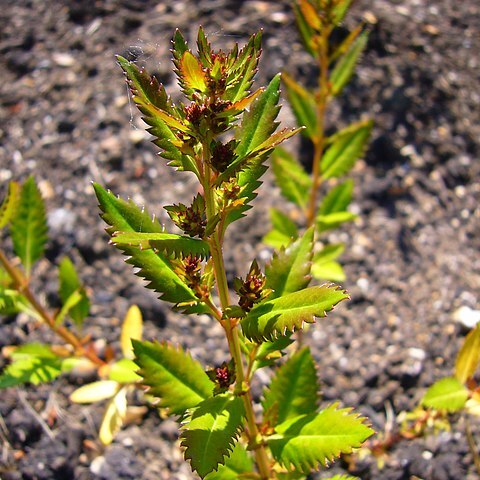
Annual or perennial herbs or subshrubs; rootstock a taproot or deeply stoloniferous. Stems smooth or 4-or 5-ribbed, glabrous or variously pilose with simple hairs. Leaves alternate or opposite, entire or serrate, glabrous or pilose. Inflorescence indeterminate and spike-like, of usually 3–7-flowered dichasia in axils of alternate bracts, with lateral inflorescences in axils of upper leaves. Flowers bisexual, 2–4-merous, shortly pedicellate. Sepals 2–4, usually smooth. Petals hooded, usually shortly clawed, keeled. Stamens twice number of petals; anthers non-apiculate, oblong. Ovary usually 4-locular (1-locular in Haloragis eyreana ), smooth or ribbed, glabrous or pilose; styles 2–4, clavate; stigmas capitate. Fruit an indehiscent nut, 2–4-locular.
Fls hermaphrodite, often strongly protandrous (? unisexual), axillary, solitary or in clusters, subtended by bracteoles and lfy bracts. Calyx-lobes 4-2, free; petals 4-2, cucullate; stamens caducous, 4, or 8 in two whorls, filaments short, anthers broad-linear; ovary 4-to 1-celled, styles 4-2, short, stigmas papillose or plumose; fr. small, ind., often winged or ribbed, sts woody, crowned by persistent calyx-lobes. Us. perennial herbs, sts partly woody; lvs opp. or alt. orbicular to lanceolate, entire, toothed, or lobed. About 70 spp.; Southern Hemisphere and extending to S. E. Asia; in N.Z. on banks and disturbed areas, gumlands and peat. Of the 7 N.Z. spp. probably all but one are endemic.