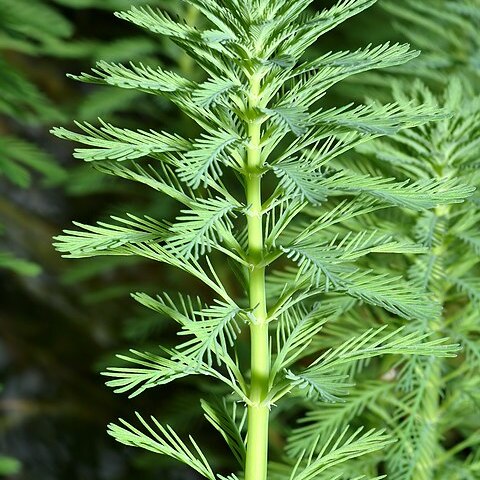
Annual or perennial aquatic or littoral herbs, monoecious or dioecious. Stems weak, glabrous (except Myriophyllum crispatum). Leaves whorled, opposite or alternate, usually dimorphic; submerged leaves pectinate; emergent leaves entire or toothed. Flowers unisexual or bisexual, 2–4-merous, solitary or in small dichasia in upper axils forming a spike-like inflorescence; bracteoles 2 (absent in M. coronatum). Male flowers at top of spike; sepals and petals usually present, petals usually hooded; stamens 1–4 or 8; ovary and styles vestigial or absent. Female flowers (monoecious plants) below males; sepals present or absent; petals vestigial or absent; stamens absent; carpels 2–4; style sessile or clavate, rarely subulate; stigma usually fimbriate. Fruit dry, variously ornamented. [The above description from the Flora of Australia Volume 18 (Orchard 1990) requires revision to include Meziella which was treated as a separate genus in the Flora at the time, but now considered a synonym of Myriophyllum-Editor, 13 July 2021.] Meziella description from (Orchard 1990): Glabrous creeping perennial herb. Stems rooting at nodes. Leaves alternate, trifid; lobes terete, with a short tooth between them. Inflorescence an indeterminate spike of flowers borne singly in the axils of leaf-like bracts. Flowers 4-merous, almost sessile. Sepals 4, linear-subulate, greatly exceeding the petals. Petals 4, hooded, sessile. Stamens 4, opposite sepals; anthers broadly linear, acute. Pistil not seen. Fruit unknown.
Annual or perennial herbs, usually glabrous, monoecious, dioecious, or fls ☿; stems rooting at nodes, prostrate to erect. Lvs usually whorled, sometimes opposite or alternate, usually dimorphic, the submerged lvs pectinate and finely divided, the aerial lvs ± entire, rarely all lvs of either form. Hydathodes often present near lf axils. Infl. a simple or rarely branched, terminal spike; fls usually solitary, in the axils of aerial lvs, occasionally in the axils of upper submerged lvs, each with 2 bracteoles; ♂ fls usually above ♀ within same infl. in monoecious spp. ♂ fls (2)-4-merous; sepals present; petals not clawed, ± hooded; stamens (1)-4 or 8; filaments short; anthers linear; pistil rudiments present or 0. ♀ fls (2)-4-merous; sepals and petals very reduced or 0; ovary (2)-4-celled; styles as many as cells of ovary; stigmas capitate, fimbriate; staminodes rudimentary. Fr. of 2-4, 1-seeded mericarps; mericarps usually smooth and rounded on dorsal face, lacking a differentiated pericarp, sessile or shortly pedunculate.
Herbs perennial, aquatic, submerged or shortly emergent, monoecious or dioecious. Stem soft, few to many branched, rhizomatous. Submerged leaves 3-or 4-whorled, rarely alternate, pectinate, ovate to oblong in outline; segments filiform; emergent leaves smaller, sometimes uppermost ones undivided, reducing to bracts of inflorescence. Inflorescence usually emergent, a terminal spike with flowers 4-whorled, or in axils of emergent leaves. Flowers subtended by a primary bract and 2 bracteoles, sessile, usually 4-merous, minute, lowermost ones female, uppermost ones male, sometimes middle ones bisexual. Male flowers: calyx deeply 2-4-lobed; petals 2-4, boat-shaped, often pink; stamens 2-8, epipetalous. Female and bisexual flowers: calyx tube united with ovary; lobes 4, minute; petals minute, often caducous or absent; ovary (2-)4-celled; style absent; stigmas 4, sessile, recurved, plumose, papillose. Fruit a schizocarp, separating into (2-)4 mericarps. Seed 1 per mericarp.
Fls hermaphrodite and strongly protandrous, or unisexual with ♂ above ♀; solitary in lf axils, subtended by bracteoles. Calyx-lobes 4 or 0, free; petals 4 or 0, cucullate, glab.; stamens 8 or 4, anthers linear; ovary 4-celled, styles 4, short, stigmas papillose or plumose. Fr. small, separating into 2-4 1-seeded mericarps. Glab. herbs of water and wet places; lvs opp., alt., or whorled, entire, toothed, or pinnately divided, submerged lvs often with capillary segs. About 40 spp., cosmopolitan. Of the 5 N.Z. spp. 2 are endemic.
Fls unisexual, 4-merous, small, sessile in the axils of bracteal or foliage lvs, often aggregated into an emersed terminal spike; cal of 4 teeth, or obsolete; pet present or not; stamens 8 or 4 (even in one sp.); fr hard, ± 4-lobed, eventually splitting into 4 mericarps; vegetatively plastic herbs, submersed in quiet water or rooting on muddy shores, usually with once-pinnately dissected lvs. 20+, cosmop.
Flowers mostly sessile, 1 or 2 in the axil of a leaf or bract in terminal, emergent spikes or solitary in the lower leaf-axils, bisexual or unisexual, monoecious or sometimes polygamous (the upper flowers commonly male, the lower female, sometimes with hermaphrodite ones in between), rarely dioecious; bracteoles 2, often inconspicuous.
Submerged leaves in whorls of 3–6 and always pinnatisect into undivided segments; aerial leaves whorled, opposite or alternate, often dentate or entire or bract-like; stipules absent; leaf-bases often accompanied by 1–3 filiform to subulate, deciduous, stipule-like outgrowths.
Gynoecium 2–4-locular, rudimentary or absent in male flowers; styles 2 or 4, very short or absent; stigmas 2 or 4, subsessile or sessile, persistent.
Petals in male flowers 2 or 4, cucullate, caducous, in female minute or absent.
Glabrous, mostly perennial, usually aquatic herbs, sometimes growing on mud.
Fruit separating into 4 (or fewer by abortion) 1-seeded nutlets.
Stems free-floating or with rooted rhizomes, mostly branched.
Stamens (2–7)8 or 1; staminodes absent in female flowers.
Calyx of 4 small lobes in male flowers, minute in female.
Seeds pendulous; testa membranous; endosperm copious.