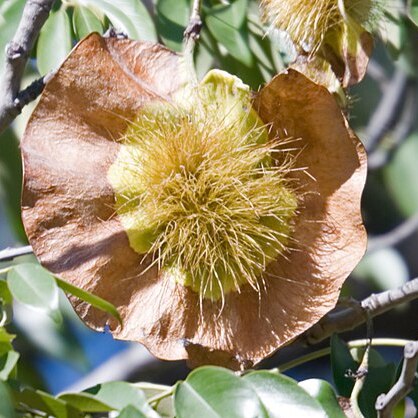
Trees. Branches spreading, glabrous to pubescent. Leaves alternate, imparipinnate; stipules small, caducous; stipels absent; leaflets alternate, rarely subopposite. Inflorescence a simple raceme to a lax, terminal or axillary panicle. Flowers yellow; bracts and bracteoles small, caducous. Pedicel articulate. Calyx often incurved, obconical, 5-toothed; teeth short, upper 2 ± connate. Corolla papilionaceous, exserted beyond calyx; petals long clawed; standard ovate to orbicular, as keel crisped on margin. Stamens 10, monadelphous to diadelphous (5+5 or 9+1), staminal sheath split open dorsally; anthers versatile. Ovary stipitate or sessile, 2-6-ovuled; style incurved, filiform, glabrous; stigma terminal. Legume indehiscent, orbicular, compressed, broadly hardened winged around margin, usually 1-seeded; style persistent, incurved. Seeds oblong or subreniform, hilum small.
Trees, unarmed. Leaves alternate, imparipinnate; stipules usually minute. Flowers in axillary or terminal racemes or panicles; bracts and bracteoles small and caducous, or large and lanceolate; hypanthium campanulate, the teeth minute; stamens monadelphous or diadelphous, the sheath open above, occassionally below, the filaments short, the anthers versatile; ovary sessile or obviously stipitate, the style slender, the stigma terminal, minute. Fruits orbicular or oval-oblong, flat, the seminiferous area median, the wing membranous to coriaceous, disposed in an elliptic, falciform or circular fashion, rarely rudimentary, the seeds usually solitary.
Stamens either all 10 connate in a dorsally-slit sheath, or 9 fused with the upper one free, or in 2 groups (phalanges) of 5; anthers dorsifixed, longitudinally dehiscent.
Standard circular or broadly obovate; wings obliquely obovate; keel petals shorter than the wings, dorsally slightly connate or free.
Leaves imparipinnate, stipulate; leaflets alternate, opposite or irregularly subopposite.
Calyx turbinate at the base, incurved; upper teeth partially connate.
Ovary few-ovulate; style somewhat incurved; stigma small, terminal.
Pod circular, broadly winged or obovate with obsolete wings.
Seed reniform or oblong-reniform; hilum small.
Inflorescence racemose or paniculate.
Flowers yellow.
Trees.