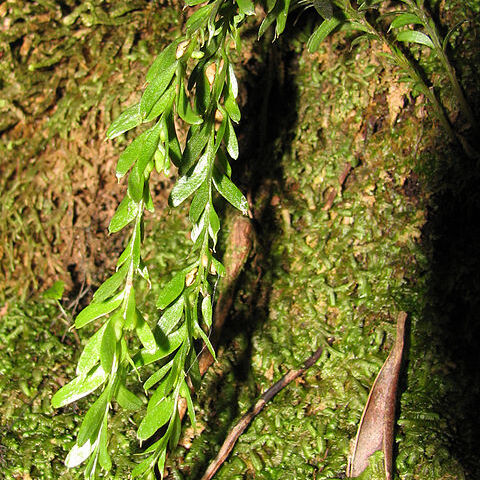
Sporangia 2-celled, coriac.; cells elongate, pointed, constricted at junction, septum across narrowest diam., terminal on short lobes that bear two lf-like lobes just below insertion of sporangium. Plant us. epiphytic, with pend. axis. Lobes ∞, lf-like, flattened laterally, decurrent, irregularly two-rowed. Lower part of aerial axis with scale-like lobes or nearly naked. One polymorphic sp.: Australia, Tasmania, N.Z., Pacific Islands.