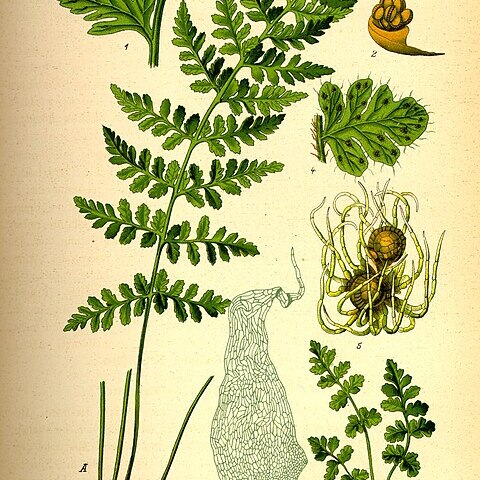
Petiole slender and wiry, shorter than the blade, scaly at least at the base, with 2 bundles, these uniting distally; blade pinnate to subtripinnate, scaly or scaleless, often hairy or glandular, the veins forking and free, not reaching the margin; sori borne on the veins, often confluent in age, rotund but with an elongate receptacle; indusium inferior, borne below and ± surrounding the sporangia, consisting variously of septate hairs around a minute basal disk, or of a small sac that soon ruptures irregularly to form a small basal disk with spreading, unequal segments; small to medium-sized ferns of rocky places, with tufted lvs and persistent, elongate petiole-bases on a short rhizome that is covered with yellowish to dark brown scales. 20–25, cosmop.