Inflorescences of axillary or terminal, elongated panicles; branches of inflorescence, calyx and corolla usually with a dense indumentum of stellate or dendroid hairs mixed with simple hairs.
Stamens 6, inserted just outside the disk, equal in size, with filaments broader towards the base (smaller and infertile in female flowers).
Petals 3, valvate or sometimes slightly imbricate, incurved, somewhat hooded and usually mucronulate at the apex.
Ovary (vestigial in male flowers) 2 (3)-locular with 2 ovules per loculus; style very short, stigma 3–4-lobed.
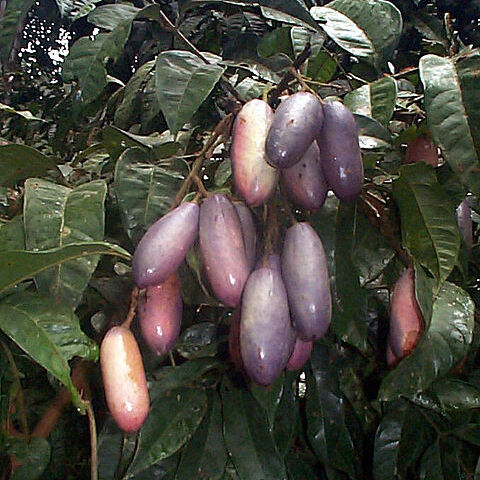
Seed large; cotyledons very much thickened and deeply folded or conduplicate, thus appearing palmately lobed.
Calyx rotate or broadly campanulate, divided almost to the base; lobes 3, valvate.
Fruit an ovoid or ellipsoid drupe; endocarp thin and cartilaginous.
Disk annular but slightly lobed between the stamens.
Leaves imparipinnate; leaflets entire.
Flowers unisexual.
Dioecious trees.