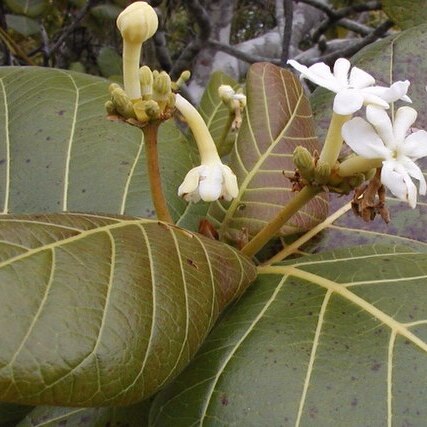
Trees or shrubs, the branches in some species armed with spines (not in Old World). Leaves opposite or rarely ternate, petiolate; stipules interpetiolar or intrapetiolar, simple, persistent or soon falling, free or connate. Flowers hermaphrodite or polygamo-dioecious, showing limited heterostyly, (4–)5–6(–9) even 11-merous, usually sessile, mostly secundly arranged in axillary pedunculate apically dichotomously branched inflorescences or rarely solitary or in groups of 2–3; bracteoles present or absent. Calyx shortly tubular, globose or ovoid, the limb truncate or 2–9-toothed. Corolla white, yellowish or red to reddish purple, salver-shaped; throat glabrous or nearly so; lobes imbricate or subvalvate, the margins often wavy or crenulate. Stamens 4–9, inserted in the throat, included; anthers sessile or nearly so, dorsifixed. Ovary 2–9-locular; ovules solitary, pendulous; style slender; stigma ± capitate, slightly bifid. Fruit globose or subglobose, ± fleshy or fibrous with woody or bony endocarp, 2–9-locular, containing 2–9 pyrenes. Seeds with little or no endosperm.
Trees or shrubs. Leaves occasionally ternate, usually petiolate; stipules de-ciduous. Inflorescences axillary, cymose, the flowers occasionally solitary, usu-ally secundly disposed or congested; bracteoles present or absent. Flowers with the hypanthium ovoid or globose, the calycine cup tubular, cupular or campan-ulate, truncate, edentate or 2-9-toothed; corolla funnelform or salverform, the tube elongate, the lobes 4-9, imbricate, 2 of them exterior; stamens 4-9, inserted in the tube, the anthers slender, dorsifixed, included, the filaments frequently wanting; style slender, the stigmas capitate or 2-lobed, the ovary 2-9-celled, the ovules 1 per cell, pendulous. Fruits drupaceous, globose, ovoid or oblong, thinly carnose, usually with a fine velvety indumentum, often acutely angular, the pu-tamen ligneous or bony, the testa membranous.
Flowers hermaphrodite or polygamo-dioecious, showing limited heterostyly, (4)5–6(9)-or even 11-merous, usually sessile, mostly secundly arranged in axillary pedunculate apically dichotomously branched inflorescences or rarely solitary or in groups of 2–3; bracteoles present or absent.
Corolla white, yellowish or red to reddish-purple, salver-shaped; throat glabrous or nearly so; lobes imbricate or subvalvate, the margins often wavy or crenulate.
Leaves opposite or rarely ternate, petiolate; stipules simple, persistent or soon falling, free but overlapping each other at apex.
Fruit globose or subglobose, ± fleshy or fibrous with a woody or bony endocarp, 2–9-locular, containing 2–9 pyrenes.
Ovary 2–9-locular; ovules solitary, pendulous; style slender; stigma ± capitate, slightly bifid.
Stamens (4)–9, inserted in the throat, included; anthers sessile or nearly so, dorsifixed.
Trees or shrubs, the branches in some species armed with spines (not in Old World).
Calyx shortly tubular, globose or ovoid, the limb truncate or 2–9-toothed.