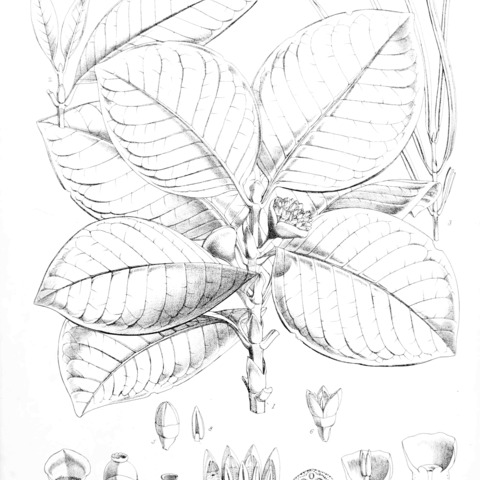
Leaves petiolate, less often subsessile or occasionally sessile; blades drying blackish-brown, slate-grey or less often dull green, typically subcoriaceous but occasionally chartaceous or coriaceous, usually glabrous, very infrequently pubescent; tertiary nerves obscure (or rarely apparent); domatia present as glabrous to pubescent cavities, or sometimes absent; stipules triangular at their base, sometimes produced into a lobe, or linear to ovate, persistent or readily caducous, with a few silky hairs and colleters inside.
Style slender, slightly longer than corolla tube, somewhat tapered at apex; pollen presenter as wide as long, 2–several-lobed, but lobes only separating to reveal stigmatic surface in female and hermaphrodite flowers, solid, attached to style at base or sometimes slightly recessed; disk annular or hemispherical; the region between the ovary and disk sometimes elongating (in Madagascan species only); ovary 2–10-locular, each loculus containing one pendulous ovule.
Corolla rather fleshy, usually drying dark with the lobes pale above; tube shorter than or longer than the lobes, throat densely congested with crisped or less often straight moniliform hairs, lacking a well-defined ring of deflexed hairs inside; lobes spreading, reflexed or sometimes erect, thickened towards the the apex, sometimes shortly apiculate, upper surface of lobes usually graniculate or very finely colliculate.
Flowers unisexual or hermaphrodite, 4-or 5-merous borne in pedunculate umbels, sometimes with both peduncle and pedicels somewhat reduced, in dioecious species the female inflorescence containing fewer flowers (often solitary) than the male; bracts paired, connate and entirely surrounding the inflorescences in bud, persistent, with silky hairs and colleters towards base inside.
Stamens set at throat; filaments short, attached near the base of the anther; anthers erect, less often spreading or rarely reflexed, ovate to oblong-ovate, the dorsal face, except for the margin, covered with darkened connective tissue, sometimes extending into a short apiculum.
Seeds narrowly obovoid with ventral area flattened and apex somewhat crested; endosperm entire; testa finely reticulate; embryo straight or slightly curved with radicle erect and cotyledons small and set perpendicular to ventral face of the seed.
Fruit yellow to red, fleshy, when 2-locular subspherical to obcordate in lateral view, or less often didymous, bilaterally flattened, often elaborated with extra lobes or flanges, when multi-locular lobes correspond to number of locules.
Calyx tube ± ovate in female and hermaphrodite flowers, and very reduced in male flowers; limb reduced to a rim, sometimes shortly dentate or bearing unequal lobes, or sometimes (in Mauritian species) cupular.
Pyrenes thinly woody to woody, ellipsoid to obovoid with ventral face flattened, crested around the apex, eventually dehiscing from the point of attachment back along the crest.
Small shrubs to medium-sized trees.