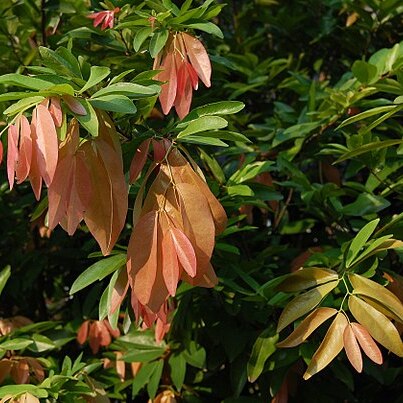
Unarmed, normally evergreen trees. Leaves simply pinnate; leaflets nearly always opposite, in one to many pairs, without gland-dots. Inflorescence paniculate or (in East Africa ? only in 4, C. brachyrrhachis and 12, C. filifera) simply racemose. Flowers hermaphrodite, spirally arranged along the inflorescence-axes; pedicels (in the Flora area, not necessarily elsewhere) jointed at apex and persistent after the flowers have fallen; bracteoles small, not enclosing the flower-buds. Sepals 4(–5), imbricate, glabrous inside, or with a few hairs near centre. Petals (4–)5, equal or nearly so. Stamens (8–)10(–12); filaments glabrous, free or almost so; anthers dehiscing by longitudinal slits. Ovary ± stipitate, ± pubescent or tomentose; ovules 1–4; style elongate; stigma minute. Pods either flattened, woody, and dehiscing elastically into 2 valves which are smooth or nearly so outside, or (typically for the genus, but not in indigenous species) indehiscent, thickened, and tubercled outside. Seeds 1–2(–4), with a very short funicle, thin-walled, exareolate.
Unarmed, usually evergreen trees. Leaves usually simply pinnate, rarely unifoliolate; stipules caducous; leaflets nearly always opposite, in 1–many pairs, asymmetric, without gland dots. Inflorescence paniculate or simply racemose. Flowers bisexual, spirally arranged along the inflorescence axes; bracteoles small, not enclosing the flower buds. Sepals usually 4, imbricate. Petals usually 5, equal or nearly so. Stamens usually 10; filaments free or almost so; anthers dehiscing longitudinally. Ovary ± stipitate, 1–4-ovulate; style elongate, central, excentric or occasionally attached to wall of receptacle; stigma minute. Fruits either thickened and indehiscent or flattened, woody and dehiscing elastically into 2 smooth valves. Seeds usually 1 or 2, with a very short funicle, thin-walled. See also Cooper (2015: 394).
Unarmed forest trees. Leaves evenly pinnate; leaflets a single pair (in Ameri-can species), oblique, subcoriaceous, eglandular. Inflorescence racemose to fascicu-late, axillary. Flowers small; calyx essentially polysepalous, the 3-5 lobes reflexed from a small, central, disc-like receptacle and often caducous, imbricate in. bud; petals 5, subequal to somewhat unequal, inserted with the stamens upon the recep-tacle; stamens 10, free, the filaments glabrous; anthers small; ovary sessile to short-stipitate, mostly free, 1-to 2-ovulate; style filiform; stigma terminal, truncate or capitate. Legume rather small, usually oblique or curved, coriaceous, swollen; seeds arillate.