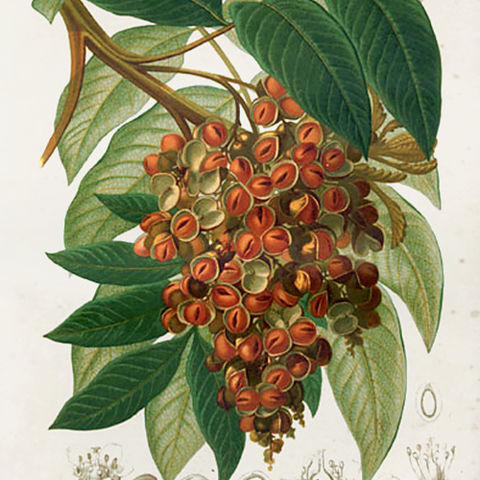
Trees, probably monoecious. Indumentum of solitary simple hairs only. Twigs terete, striate, fulvous-tomentellous, tardily glabrescent. Leaves paripinnate, 4-or 5-jugate (Malesian species); no pseudostipules; neither petiole nor rachis winged; leaf axes hairy like the twigs. Leaflets alternate (Malesian species), above without wax, beneath without papillae and red glands, entire, usually (Malesian species always) hairy; base symmetrical or sometimes slightly oblique; midrib above prominulous, beneath prominent, nerves prominent beneath, veins and veinlets prominulous on both sides. Inflorescences axillary, terminal ones together pseudoterminal, thyrsoid, mostly sparsely branched with divaricate branches, densely hairy like the twigs. Flowers unisexual, actinomorphic or ± zygomorphic, white to cream. Sepals 5, free or nearly so, equal, not petaloid, outside hairy, inside hairy or glabrous. Petals 4 or 5, as long as or slightly longer than the calyx, relatively long-clawed, (sub)glabrous, inside with 2 hairy scales, crested or not. Disc uninterrupted to interrupted (Malesian species), glabrous. Stamens usually 8, exserted; filaments hairy in the lower half; anthers glabrous, basifixed, dehiscence latero-introrse. Ovary slightly 3-lobed, sessile, densely tomentellous, 3-locular, each locule with 1 ovule; style terminal, long and slender, very sparsely hairy; stigma grooved or slightly lobed. Fruits capsular, 3-lobed, not stipitate, smooth, tomentellous, glabrescent or not, not winged, completely 3-celled, loculicidal, inside sericeous. Seeds thick to thin lenticular, completely enveloped by a 2-lobed arillode, the latter without basal extension.
More
Trees. Branchlets usually hairy, lenticellate. Leaves paripinnate; leaflets usually large, opposite or alternate, thinly coriaceous, entire. Panicles axillary; cymules usually sessile; bracteate. Flowers polygamous, regular or slightly irregular, small. Calyx either shortly cupular with 5 lobes, or of nearly free lobes and imbricate. Petals 4 or 5, the 5th usually reduced, broadly ovate, clawed, glabrous; scales bilobed, hairy, usually crested. Disc usually incomplete, glabrous. Stamens 6–10; filaments usually hairy. Ovary 3-locular, with 1 ovule per locule; style stout. Fruit usually large, subglobose to transversely ellipsoidal, 1–3-lobed, loculicidally dehiscent; valves usually hairy. Seeds subglobose, slightly compressed; aril thick, fleshy, bilobed, usually red, acidic, nearly enveloping seed.