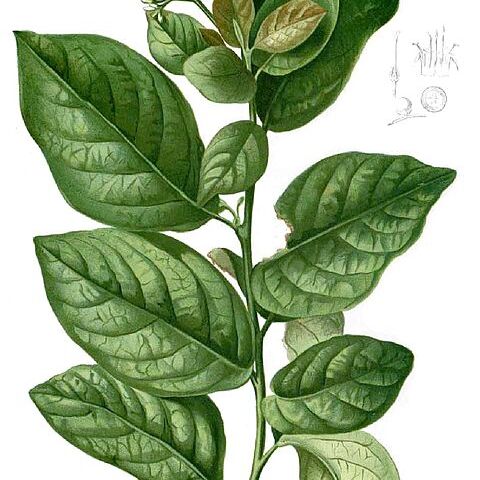
Trees or shrubs. Leaves small to large, alternate, margin entire or serrate, sometimes wavy. Inflorescences terminal and/or lateral, branched or unbranched, sometimes arranged in corymb-or panicle-like structures. Calyx-lobes 5, separate from the beginning. Corolla white or pale yellow, with elongate-cylindrical or campanulate tube and spreading to recurved lobes. Stamens: anthers exserted as a rule, on filiform filaments. Ovary: style terminal, with two branches free in the uppermost part or to the middle; stigmas 2, capitate or elongate. Fruit a subglobose drupe, yellow, orange or reddish, with two separate pyrenes sometimes divided again into 4 one-seeded parts. Pollen spheroidal to prolate-spheroidal or subprolate, finely reticulate or striate-reticulate, 3-colpate or 3-colporoidate. Fig. 6.
Trees or shrubs. Leaves alternate, simple, pinnately-nerved, entire or dentate; mostly petiolate. Iiflorescences paniculate or cymose, mostly terminal. Flowers perfect, + actinomorphic, subsessile to pedicellate; calyx of 5 sepals, open in bud, free or somewhat connate basally; corolla ? funnelform, small, white, 5-lobed, the lobes spreading; stamens 5, mostly exserted, the anthers linear or broadly oblong; ovary 2-or 4-locular, the style bifid near the tip, the stigmas 2, and capitate or clavate. Fruit drupaceous, mostly spherical, with one 4-loculed and 4-seeded stone, with two 2-loculed, 2-seeded stones or with 4 separate stones.
Trees or shrubs. Leaves petiolate, entire or serrate at margin. Inflorescences corymbose or paniculate-cymose. Calyx 5-lobed. Corolla white or pale yellow, tubular or tubular-campanulate, rarely funnelform, 5-lobed; lobes spreading or reflexed. Filaments usually exserted; anthers ovate to oblong or linear. Ovary ovoid, 2-loculed, each locule with 2 ovules. Style terminal, 2-cleft; stigmas 2, capitate or elongated. Drupes yellow, orange, or pale red, subglobose, glabrous, endocarp divided at maturity into 2 2-seeded or 4 1-seeded pyrenes.
Trees or shrubs, glabrous or hairy. Leaves alternate, usually petiolate. Inflorescence usually paniculate or corymbose, axillary or terminal, bracteate or not. Flowers bisexual. Calyx lobes joined at base. Corolla hairy outside or glabrous, white or yellow. Stamens exserted. Style terminal, divided above middle into 2 long arms; stigmas capitate or elongate. Fruit a globose drupe, splitting into 1-or 2-seeded pyrenes, usually yellow, orange or red.
Ovary 2-or 4-locular; style terminal, ± deeply divided into 2 branches, topped by capitate or umbilicate stigmas.
Corolla tube cylindrical to widely funnel-shaped; lobes 5(6), imbricate, oblong, spreading or reflexed.
Stamens 5(6), inserted at the corolla-throat, exserted; anthers oblong or sagittate.
Leaves alternate, usually petiolate, simple, entire, dentate, crenate or serrate.
Flowers hermaphrodite or polygamous, actinomorphic, subsessile or pedicellate.
Fruit drupaceous, subglobose; endocarp of usually 4, 1-seeded pyrenes.
Inflorescences paniculate or corymbose, usually terminal.
Calyx 5-lobed, deeply divided, lobes imbricate in bud.
Trees or shrubs.