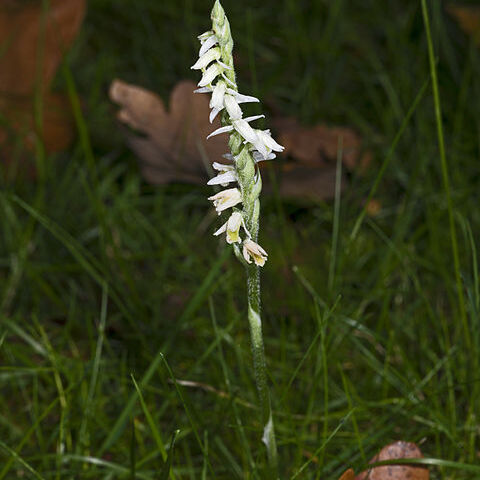
Herbs, terrestrial, acaulescent. Roots fasciculate, fusiform, fleshy, glabrous. Leaves basal, forming a rosette, linear, elliptic, or broadly ovate, rarely subcylindric, base sheathing. Inflorescence terminal, racemose with many small flowers arranged spirally around rachis. Flowers resupinate, horizontal or nodding, not opening widely, small; ovary twisted, fusiform. Sepals free, narrowly elliptic to lanceolate, subsimilar; dorsal sepal erect, often connivent with petals and forming a hood; lateral sepals dilated or sometimes saccate at base. Petals erect, oblanceolate, recurved; lip entire or obscurely 3-lobed, shortly clawed, apex recurved, undulate, lateral margins embracing column; disk usually papillose, with 2 fleshy glands at base. Column clavate, ventrally pubescent; anther erect, 2-locular, on dorsal surface of column; pollinia 2, each 2-partite, granular-farinaceous, with or without short caudicle and attached to narrow viscidium; rostellum erect, 2-lobed at apex after removal of viscidium; stigma suborbicular to elliptic. Capsule ellipsoid.
Small, or rarely large, terrestrial (rarely epiphytic) herbs with basal or cauline leaves or both, or leafless. Roots often fleshy, fasciculated or tuberous. Leaves various, produced before, with, or after, the flowers. Sepals free; dorsal sepal usually erect and forming a galea with the petals; lateral ones erect or spreading, affixed to the summit of the ovary, decurrent and forming a free or adnate mentum. Petals usually narrow and usually coherent to the dorsal sepal. Lip sessile or clawed, plane, concave or gibbous, simple or lobed, in some species bi-caudate at the base, adherent to the column in almost all the species, ecallose or callose. Column terete; clinandrium often membranaceous and conspicuous, often continued into the rostellum; rostellum various, inconspicuous or conspicuous, truncate and retuse to lobed to aristate; anther dorsal, erect, sessile or stipitate; pollinia 2, powdery or granular, usually attenuated at one end.
Fls ∞ in ± spirally twisted spike; floral bracts = or > ovary. Ovary and per. ± glandular-pubescent; per. ± horizontal-tubular, dorsal sepal uppermost; lateral sepals subsimilar, not connate; petals ± similar, in part adnate to dorsal sepal. Labellum of about equal length, sessile or shortly clawed, concave and embracing base of column, distally spreading and crenate to crisped; calli 2, lateral, near base. Column short, us. flanked by 2 small wings; anther dorsal, often overtopped by rostellum, pollinia 2 per cell, pollen granular; stigma broad; rostellum us. long, remaining as 2 tall processes after its central long-oval viscidium is detached. Plants terrestrial, glab. except for infl.; roots clustered, us. ± tuberous. Lvs several, mostly basal; stem with persistent sheathing bracts Spp. estimated at 50 to 300, widely dispersed through temperate zones. The N.Z. sp. widespread in Australia and Asia.
Herbs, perennial, terrestrial. Roots fleshy, fasciculate, slender to tuberous. Stems with foliaceous sheaths. Leaves basal or occasionally cauline. Inflorescences terminal spikes, flowers inserted in lax to dense, ± evident spiral, pubescent to glabrous, often glandular. Flowers resupinate, often somewhat apically recurved, white, cream, or yellow (pink in S. sinensis); perianth parts distinct or sepals basally connate, connivent; lip lanceolate to ovate or pandurate, rarely linear, fleshy to somewhat membranaceous, base with pair of calli, apex usually ± crisped; mentum or spur absent; column short, cylindric; anther cordate, apex acute or obtuse; pollinia clavate with slender viscidium; ovary sessile, cylindric.
Terrestrial, evergreen or facultatively deciduous orchids with thick, fleshy roots. Leaves smooth, narrow, in a loose basal rosette. Inforescence tall, wiry, spicate. Flowers small, colourful, densely crowded in a spiral spike. Basal part of dorsal sepal and petals overlap loosely to form a galea which partially hoods the labellum. Lateral sepals free, porrect to spreading. Labellum flexibly attached to anterior base of column. Labellum lamina 3-lobed, protruding shortly from flower; base tubular, with 2 rounded or tonsil-like glands; distal and apical margins wavy to frilly. Column slender.