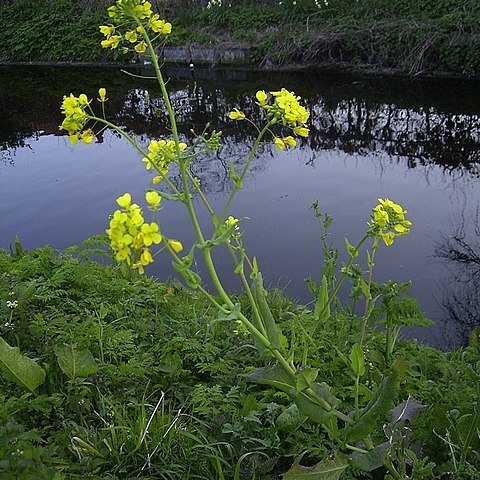
Annuals, biennials, or, rarely, perennials; not scapose; glabrous, glabrescent, or pubescent. Stems erect, unbranched or branched distally. Leaves basal and cauline; petiolate or sessile; basal (persistent in B. tournefortii), rosulate or not, petiolate, blade margins entire, dentate, or lyrate-pinnatifid; cauline petiolate or sessile, blade (base sometimes auriculate or amplexicaul), margins entire, dentate, lobed, or sinuate-serrate. Racemes (corymbose), considerably elongated in fruit. Fruiting pedicels erect, spreading, ascending or divaricately-ascending, often slender. Flowers: sepals usually erect or ascending, rarely spreading, oblong [ovate], lateral pair usually saccate basally; petals yellow to orange-yellow [rarely white], obovate, ovate, elliptic, or oblanceolate, claw often differentiated from blade, (sometimes attenuate basally, apex rounded or emarginate); stamens tetradynamous; filaments slender; anthers oblong or ovate, (apex obtuse); nectar glands confluent or not, median glands present. Fruits siliques, dehiscent, sessile or stipitate, segments 2, linear, torulose or smooth, terete, 4-angled, or latiseptate; (terminal segment seedless or 1-3-seeded, usually filiform or conic, rarely cylindrical); valves each prominently 1-veined, glabrous; replum rounded; septum complete; ovules [4-]10-50 per ovary; stigma entire or 2-lobed. Seeds uniseriate, plump, not winged, globose; seed coat (reticulate or reticulate-alveolate), mucilaginous or not when wetted; cotyledons conduplicate. x = 7, 8, 9, 10, 11.
Annual, biennial or perennial herbs, rarely subshrubs, glabrous or with hispidulous simple hairs. Leaves undivided to pinnatipartite. Racemes terminal, usually ebracteate, corymbiform to paniculate, with many rather large flowers, in fruit elongate, lax. Sepals erect, connivent or spreading, the inner larger and somewhat saccate. Petals yellow or white, spathulate to clawed. Stamens 6, the lateral ones often ascending; filaments linear. Lateral nectaries prismatic or reduced, median ones semiglobose to filiform, often large. Ovary cylindrical, sometimes on a a gynophore; stigma semi-globose to slightly bilobed; ovules numerous, usually uniseriate. Fruit a siliqua, readily dehiscent, terete or slightly laterally compressed, in transverse section ± biconvex, attenuate into a conical to filiform beak with 0–3 seeds; valves rather thick, convex, with prominent midnerve and inconspicuous side-nerves. Seeds usually globose, reticulate, not mucilaginous.
Annual, biennial or perennial herbs, rarely subshrubs, glabrous or with hispidulous simple hairs. Leaves undivided to pinnatipartite. Racemes terminal, usually ebracteate, corymbiform to paniculate, with many rather large flowers, in fruit elongate, lax. Sepals erect, connivent or spreading, the inner larger and somewhat saccate. Petals yellow or white, spathulated to clawed. Stamens 6, the lateral ones often ascending, filaments linear. Lateral nectaries prismatic or reduced, median ones semiglobose to filiform, often large. Ovary cylindrical, sometimes on a gynophore; stigma semiglobose to slightly bilobed, ovules numerous, usually uniseriate. Fruit a siliqua, readily dehiscent, terete or slightly laterally compressed, in transverse section ± biconvex, attenuate into a conical to filiform beak with 0—3 seeds; valves rather thick, convex, with prominent midnerve and inconspicuous side-nerves. Seeds usually globose, reticulate, not mucilaginous.
Sep usually erect to ascending, saccate at base; pet yellow (our spp.), obovate, clawed; staminal glands 4, rounded, evident; anthers oblong; ovary subcylindric, scarcely narrowed to the short style; ovules several or many in one row in each locule; stigma capitate; fr subterete or angled, ± elongate, often torulose, terminated by a sterile, slender, terete to angular beak, this nerveless or 1-nerved on each side; valves with a prominent midnerve, the other nerves much weaker, scarcely parallel, often anastomosing; cotyledons conduplicate; seeds large, subglobose, in one row in each locule; coarse, weedy annuals and biennials, at least the lower lvs pinnatifid, the fls usually conspicuous. Dwarf specimens of all our spp. occur under unfavorable conditions and are not provided for in the descriptions. 35, Old World.
Plants annual or biennial, glaucous, glabrous or with scattered simple hairs. lnflorescence ebracteate. Sepals erect or somewhat spreading, dimorphic, slightly saccate. Petals clawed, obovate, yellow. Stamens 6, free; nectariferous glands inside base of outer (short) stamens and in front of each pair of inner (long) stamens. Ovary usually sessile; style short; stigma large, attenuate, depressed-capitate, more or less bilobed. Fruit a siliqua, pedicellate, terete to somewhat flattened, dehiscent; valves with one prominent midvein and less distinct lateral net-veins; beak conical with few or no seeds; seeds numerous in valve region, one row per locule, globular or spherical, mucous; testa alveolate; cotyledons conduplicate; radicle incumbent.
Annual to perennial taprooted herbs, rarely shrubs. Hairs simple, usually bristly, sometimes 0. Stems erect or ascending, usually leafy. Lvs lyrate-pinnate, pinnate, lyrate-pinnatifid, pinnatifid, or not lobed; margin crenate or serrate. Racemes usually ebracteate. Sepals erect to patent; inner pair ± saccate at base. Petals yellow or white. Stamens 6, without appendages. Lateral nectaries 2, behind bases of lateral stamens; median nectaries 2, in front of paired stamens. Style short; stigma capitate or slightly 2-lobed. Silique linear to narrow-oblong, dehiscent; valves with strong median and weaker lateral veins; beak tapering or elongated, 0-3-seeded. Seeds almost spherical, not winged, finely reticulate, in 1 row per locule.
Annual or biennial herbs, glabrous or pubescent with simple trichomes; stems usually single from the base, branched above; leaves sessile or petiolate, simple to somewhat divided; inflorescence racemose, ebracteate; sepals oblong to slightly broader, outer pair slightly saccate; petals yellow, spatulate; siliques linear, slightly flattened parallel to replum, usually sterile above and forming a tapering beak; seeds globose or-nearly so, wingless; cotyledons conduplicate.
Fruit a beaked silique with convex valves, each valve with 1 prominent vein, beak with 0–3 seeds.
Annual or biennial (rarely perennial) herbs, glabrous or with simple hairs.
Flowers usually yellow, pedicellate, in ebracteate racemes.
Sepals erect, inner pair ± saccate.
Seeds 1-seriate, subspherical.
Cotyledons conduplicate.
Petals 4, unguiculate.
Stamens 6.