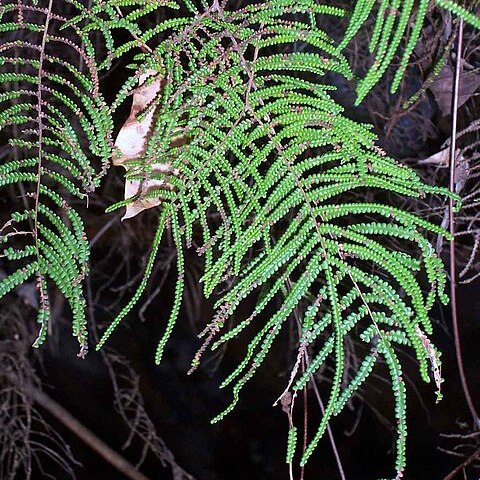
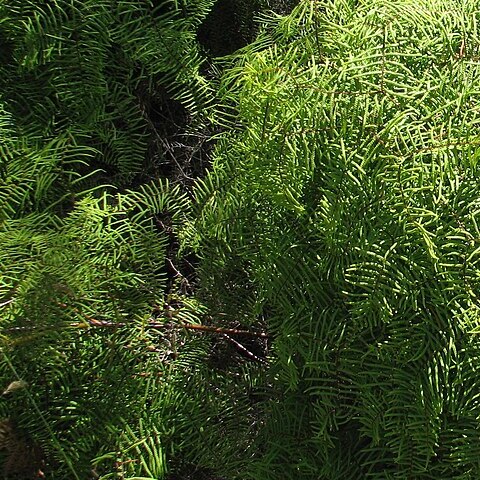
Rhizome long-creeping, thin and wiry, bearing sparse to numerous entire to ciliate scales, glabrescent; roots with prominent broad hexagonal cells. Fronds variable, often forming dense tangled masses of interlacing branches, consisting of 2–4 (–8) tiers of opposite branches with dormant vegetative buds between them (except in G. abscida ); lower primary branches sometimes dividing again. Stipes clustered or scattered along rhizome; rachis glabrous or bearing stellate hairs and/or ciliate scales. Pinnules linear, reducing in size towards the distal end of branches, glabrous or with hairs and ciliate scales on midrib; ultimate segments small, ± at right angles to costa, opposite to alternate, flat to revolute or distinctly pouched; venation open, dichotomous; ultimate veins once-forked. Sori of 2–4 large naked sporangia, on distal side of bases of ultimate segments. Spores trilete, tetrahedral; surface smooth to slightly rugose.
Characters as given for family; fronds always bipinnate or more compound.