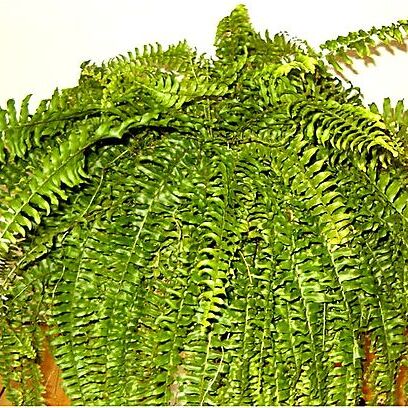
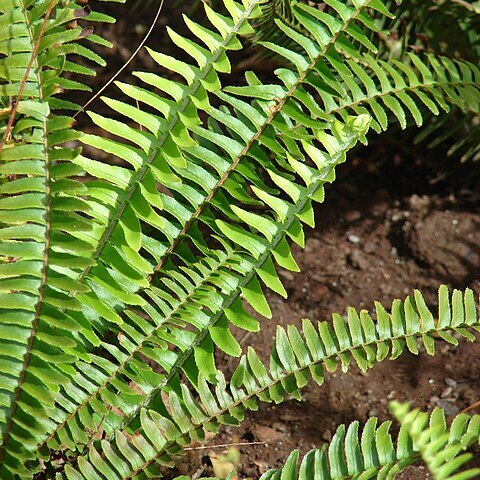
Terrestrial or epiphytic ferns. Rhizome short, erect or decumbent, densely scaly, producing numerous lateral wiry stolons which initially bear tapering elongate scales with peltate bases and marginal hair-like processes. Fronds tufted, simply pinnate, often dimorphic. Stipes tufted, much shorter than lamina, not articulated to rhizome; stipe and rachis grooved on upper surface. Pinnae sessile, articulated to rachis, usually lanceolate to falcate; acroscopic margin at base often auriculate; fertile pinnae narrower; lower pinnae sterile, shorter and more widely spaced; venation open, simple or forked; hydathodes prominent on upper surface of pinnae at vein endings. Sori superficial (rarely marginal) at vein endings; indusium reniform to round, rarely linear. Spores bilateral; surface tuberculate to rugose.
Rhizomes small, erect, densely scaly, producing numerous far-creeping runners; runners scaly but lacking tubers. Stipes 3-15 cm long. Stipes and rachises pale brown, brittle, bearing pale brown hair-like scales. Laminae almost parallel-sided, tapering only slightly towards the apex, 25-65 × 2.5-5-(6) cm, pinnate, tending to droop. Primary pinnae in > 50 pairs, overlapping in middle of frond, more widely spaced at base, the longest 1-3 × 0.5-1 cm, ± glabrous, oblong or narrowly oblong with a basal acroscopic lobe; apices obtuse; margins ± entire or slightly crenate or serrate. Sori round, in single rows either side of midrib, protected by crescent-shaped indusia.
Plants terrestrial or epiphytic. Rhizome erect, short, dictyostelic, producing long wiry stolons and sometimes tubers giving rise to new plants. Stipe tufted; lamina pinnate; pinnae sessile, articulate to rachis, lanceolate or falcate, base usually asymmetrical, often auriculate on upper side, margin crenate. Sori orbicular, terminal on a veinlet; indusia orbicular-reniform, often with a narrow sinus or lunulate, with broad sinus. x = 41.
Sori dorsal to marginal, terminal on veinlets, round to elongate. Indusium attached at base; sporangia of mixed maturation; annulus us. conspicuous, vertical, incomplete; spores bilateral. Rhizome condensed, often emitting stolons, paleate. Fronds not articulated to rhizome, paleate and often hairy, pinnate. Pinnae articulated to rhachis, veins free. About 30 spp., mostly pantropical, but extending to Japan and N.Z.
Terrestrial or epiphytic ferns. Rhizomes erect, scaly, often producing wiry runners and tubers. Fronds 1-pinnate, brittle, scaly at least on stipes; veins free. Sori round, borne on vein-endings near lamina margin, protected by ± round, reniform, or crescent-shaped indusia attached basally. Spores monolete.
Stipes not jointed to rhizome.