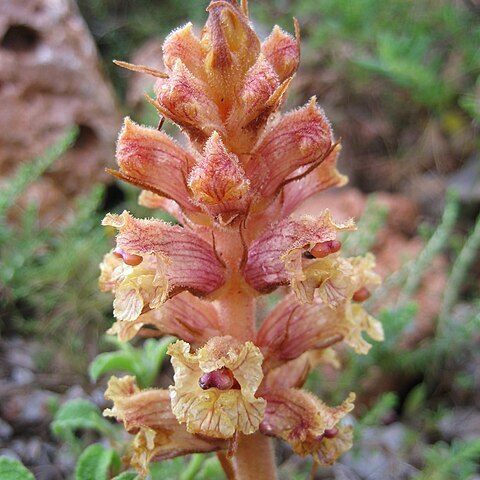
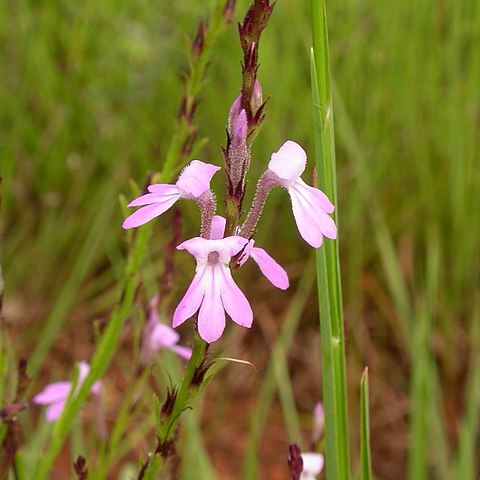
Leafless, scapigerous, parasitic herbs subsisting by attachment to roots of other plants; variously and sometimes beautifully coloured, but without chlorophyll thus never green. Stems erect, scaly, sometimes fleshy, simple or branched, glabrous to glandular-hairy. Inflorescence in East African species a cylindrical spike or spiciform raceme. Flowers hermaphrodite, zygomorphic, subtended by scale-like bracts with or without bracteoles. Calyx hypogynous, persistent, tubular (long-sided) or campanulate (short-sided), sessile or stalked, 2–5-lobed or-toothed, gamosepalous or split dorsally and ventrally into two free sections. Corolla hypogynous, gamopetalous, tubular, limbate, sometimes funnel-shaped above, curved throughout or in part. Stamens didynamous, inserted at or below the middle of the corolla tube; filaments filiform, glabrous to glandular hairy; anther cells in pairs, attached to the filament dorsally, longitudinally dehiscent, glabrous to densely lanate. Ovary superior, unilocular, bi-(rarely tri-) carpellary; placentas 4, parietal, separate to partially fused; style bilobed, peltate, orbicular or funnel-shaped. Capsule usually bivalved, ovoid-ellipsoid or ovoid-spheroid, loculicidally dehiscent; seeds small, numerous, obscurely rounded
Herbs annual, biennial, or perennial parasites, without chlorophyll. Stems unbranched or sometimes branched. Leaves scalelike, spirally or subimbricately arranged. Inflorescences racemose, spicate, or subcapitate, rarely 1-flowered; bract 1, usually similar to leaves; bractlets 2, adnate to base of calyx or pedicel. Flowers bisexual, subsessile or pedicelled. Calyx tubular, cupular, or campanulate, (3 or)4-6-lobed, 2-6-parted, 6-toothed, or spathelike, sometimes absent or of 3 free sepals. Corolla bilabiate, usually curved, sometimes tubular-campanulate or funnelform with 5 subequal lobes; upper lip entire, emarginate, or 2-lobed; lower lip 3-lobed. Stamens 4, didynamous, inserted at base of corolla tube; filaments slender; anthers 2-celled, dehiscing longitudinally, sometimes 1 cell fertile and another sterile or reduced to spur. Pistil 2-or 3-carpellate; ovary superior; placentas 2-4 or 6(-10), parietal or sometimes axile at ovary base; ovules 2-4 or numerous, anatropous. Style long; stigma inflated, discoid, peltate, or 2-4-lobed. Capsule usually dehiscing loculicidally by 2 or 3(or 4) valves. Seeds minute, testa pitted or reticulate.
Stamens 4, didynamous, inserted below the middle of the corolla-tube, alternate with the lobes, the fifth (adaxial) one reduced to a staminode or absent; anthers often connivent in pairs, opening lengthwise
Herbs, parasitic on roots, often covered with scales at the base, never green; stems with alternate, often crowded, scales
Corolla gamopetalous, often curved; limb oblique or 2-lipped, lobes 5, imbricate, the adaxial 2 interior
Ovary superior, 1-celled, with 4 parietal placentas; style terminal; ovules numerous
Flowers solitary in the axils of bracts, often crowded, hermaphrodite, zygomorphic
Calyx 4-5-toothed or lobed or variously split, lobes open or valvate
Seeds very numerous, small, with fleshy endosperm and minute embryo
Capsule often enveloped by the calyx, opening by 2 valves