Herbs, shrubs, or rarely trees. Leaves opposite or rarely alternate, whorled or basal, rosette forming; exstipulate; usually simple, rarely shallowly to deeply lobed, pinnately or rarely palmately veined. Inflorescences usually cymes, rarely racemes, axillary, often near apex and appearing terminal; usually pedunculate. Flowers perfect, zygomorphic, seldom actinomorphic. Calyx actinomorphic, rarely zygomorphic; usually (4 or)5-divided. Corolla gamopetalous, zygomorphic, rarely actinomorphic; usually 2-lipped. Fertile stamens 2 or 4, then often didynamous, rarely 5, epipetalous; anthers free or coherent, thecae 2, parallel, divergent, or divaricate; staminodes 1-3 or absent. Disc ringlike to cupular, rarely absent. Ovary superior in all Old World taxa [half inferior, or inferior], 1-loculed; gynophore seldom present; placentas (1 or)2, parietal, rarely 2-loculed, placenta 1 per locule and axile; ovules numerous, anatropous. Style 1; stigmas 1 or 2. Fruit usually capsular, loculicidal, septicidal, or circumscissile, rarely a berry, indehiscent. Seeds numerous, fusiform to ellipsoid or ovoid, minute, sometimes with appendages at 1 or both ends, with or without endosperm; embryo straight, cotyledons equal or unequal after germination.
Inflorescence generally of open axillary cymes, the flowers at each dichotomy being paired and opening serially; occasionally much congested and sub-capitate, or pseudoracemose
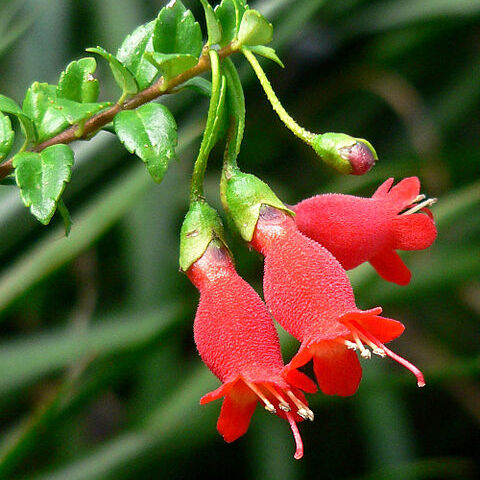
Flowers hermaphrodite (very rarely unisexual) often protandrous, usually zygomorphic, often large and showy, sometimes cleistogamous with reduced corolla
Corolla gamopetalous with distinct tube, often 2-lipped, proportion of lobes to tube variable; lobes imbricate, and adaxial pair often interior
Seeds numerous, small, more or less ellipsoid, sometimes tailed with hair-like appendages at either end; endosperm absent or very slight
Leaves opposite (rarely alternate), those of a pair equal or unequal; plants sometimes 1-foliate and the leaf cotyledonary in origin
Stamens rarely 5, usually 4 or 2, inserted on corolla-tube; anthers free or variously connate, 2-celled, opening lengthwise
Ovary superior, 1-celled with 2 parietal bilamellate placentas, occasionally 2-celled by their union centrally
Fruit a capsule (often linear, sometimes spirally twisted) or a more or less fleshy berry
Calyx tubular and 5-lobed or divided to the base or 3 upper lobes only united
Disk annular or cup-like, often lobed or undulate, rarely oblique
Acaulescent or caulescent herbs, or rarely shrubs
Ovules numerous