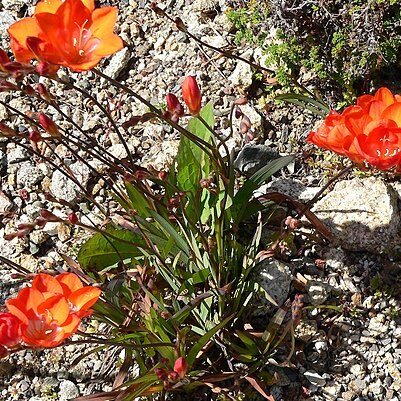
Perennial herbs with annual leaves and flowers. Corm globose; tunic fibrous. Leaves several, basal and near-basal, falcate or lanceolate to linear, flat, glabrous. Scape terete, rarely branched. Spike secund or sub-distichous, erect or bent to one side. Bracts truncate, shortly dentate, membranous-herbaceous to scarious, sub-equal, the inner shortly bifid. Flowers actinomorphic to zygomorphic. Perianth tube narrow at base, widened above; lobes longer than tube, equal or bilabiate with the dorsal lobe largest and hooded. Stamens equilateral or unilateral; anthers included, sub-basifixed to versatile, curved, often unilateral. Style branches 3, entire, recurved, filiform or expanded at apices. Capsules ellipsoid to ovoid, trigonous, membranous. Seeds numerous.
Summer-green perennial. Corm globose; tunic fibrous. Stem firm. Leaves distichous, narrow-ensiform. Inflorescence simple or branched, few-to many-flowered. Flowers white, cream, rose, orange or scarlet, each within 2 membranous spathe-valves; tube short, straight, cylindrical below, funnel-shaped above; lobes ± equal. Stamens asymmetric. Style-branches entire. Capsule oblong. Seeds many. Spp. c. 55 of tropical and S. Africa. Adventive spp. 2.
Leaves several to many, the lower 2 entirely stem sheathing (cataphylls); foliage leaves mostly basal, or the upper ones cauline, blades mostly plane (sometimes terete or H-shaped in section outside the Flora Zambesiaca area).
Flowers often orange, or yellow, pink or purple, actinomorphic or zygomorphic; perianth tube short to long, tepals subequal or bilabiate with the lower 3 often each bearing an adaxial tooth-like callus in the midline.
Inflorescence an erect or inclined spike: floral bracts membranous to scarious, the outer often 3-dentate, the inner 2-dentate and shorter than, or about as long as, the outer.
Perennial herbs with globose corms, aerial parts dying back annually; corms with fibrous tunics.
Stamens usually unilateral and arcuate (symmetrical in one S African spp.).
Style 3-branched, the branches filiform becoming somewhat broadened above.
Capsules globose to ellipsoid, more or less membranous.
Seeds numerous per locule, angular to globose.