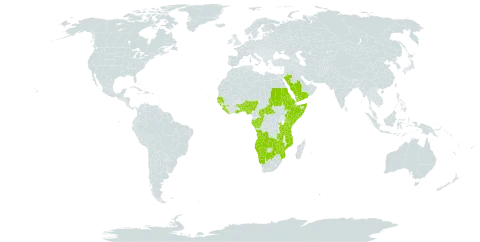
Dioecious shrubs with a simple indumentum. Twigs lenticellate. Buds perulate, the perulae subcoriaceous-scarious, persistent at the bases of the shoots. Leaves alternate, shortly petiolate, stipulate, simple, glandular-crenate or-dentate, firmly membranous or thinly chartaceous, penninerved. Stipules often accrescent, persistent, indurate, and sometimes spinescent, but occasionally deciduous. Inflorescences axillary, solitary or fasciculate, sessile or pedunculate, glomerulate or racemose, rarely subpaniculate, bracteate, bracteolate, the bracteoles in the ♂ inflorescences usually many-flowered, in the ♀ 1(–3)-flowered, or bracts and bracteoles absent. Flowers small or minute, pedicellate, the pedicels capillary, articulate usually near the base. Male flowers: calyx closed in bud, usually subglobose, apiculate, later splitting into 3–4(–5) valvate lobes; petals 0; disc glands extrastaminal, free or connate and annular, or interstaminal and free, or both, generally hirsute; stamens (2–)10–40(–60), filaments free, anthers erect, 2-thecous, extrorse, basifixed, the thecae obovoid or subglobose, free except at the base, longitudinally dehiscent; pistillode 0. Female flowers: calyx 2(–4)-partite, the lobes imbricate, smaller than in ♂; petals 0; disc-glands 2(–3), free or contiguous, flattened or clavate, with or without minute intercalated supernumerary glands, or disc shallowly urceolate and bilobate or subentire; ovary 2–3-locular, with 1 ovule per locule; styles 2–3, free or slightly connate at the base, spreading, stigmas smooth, papillose, lobulate, fimbriate or plumose-laciniate. Fruit dicoccous, didymous, or sometimes tricoccous or by abortion monococcous, loculicidally dehiscent; cocci subglobose; endocarp coriaceous. Seeds ± spherical, enveloped in a thin, fleshy, viscid, usually scarlet aril; testa crustaceous, foveolate-reticulate or ± smooth; albumen fleshy; embryo axile, radicle conical, cotyledons broad, flat.
More
Female flowers: calyx 2–4-partite, the lobes imbricate; petals absent; disk glands 2–3, free or contiguous, with or without minute intercalated supernumerary glands, or disk shallowly urceolate; ovary 2–3-locular, with 1 ovule per loculus; styles 2–3, free or slightly connate at the base, spreading, stigmas smooth, papillose, lobulate, fimbriate, laciniate or plumose.
Male flowers: calyx closed in bud, later splitting into 3–4(5) valvate lobes; petals absent; disk glands extrastaminal, free or connate, interstaminal and free, or both, generally hirsute; stamens 2–60, filaments free, anthers erect, 2-celled, extrorse, basifixed, the cells obovoid-subglobose, ± free, apically dehiscent; pistillode absent.
Seeds subglobose, thinly arillate; aril usually scarlet; testa crustaceous, foveolate-reticulate or ± smooth; albumen fleshy; embryo axile, radicle conical, cotyledons broad, flat.
Inflorescences axillary, solitary or fasciculate, sessile or pedunculate, glomerulate, racemose or subpaniculate, usually bracteate and bracteolate.
Stipules often accrescent, persistent, hardened, sometimes spinescent, occasionally deciduous.
Fruits 1–3-coccous, loculicidally dehiscent; cocci often subglobose; endocarp coriaceous.
Buds perulate (furnished with protective scales), the perulae crustaceous, persistent.
Leaves alternate, petiolate, stipulate, simple, glandular-toothed, penninerved.
Flowers small or minute; pedicels capillary, jointed.
Dioecious shrubs with a simple indumentum.