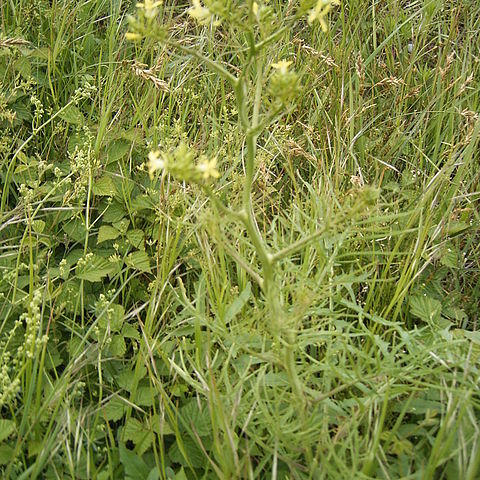
Plants not scapose; pubescent or glabrous. Stems often erect, sometimes ascending, rarely subprostrate or decumbent, often branched distally, sometimes unbranched. Leaves basal and cauline; petiolate or sessile; basal rosulate or not, petiolate, blade margins dentate, sinuate, lyrate, runcinate, or pinnately lobed [entire]; cauline similar to basal, (blade smaller distally). Racemes (several-flowered), often considerably elongated in fruit. Fruiting pedicels ascending, divaricate, or erect, slender or stout (sometimes as wide as fruit). Flowers: sepals ovate or oblong, (glabrous or pubescent); petals yellow, obovate, spatulate, oblong, or suborbicular, (longer than sepals), claw differentiated from blade, (subequaling or longer than sepals, apex obtuse or emarginate); stamens tetradynamous; filaments not dilated basally; anthers oblong, (apex obtuse); nectar glands confluent, subtending bases of stamens, median glands present. Fruits usually sessile, rarely shortly stipitate (gynophore to 1 mm), usually linear, rarely lanceolate or subulate, smooth or torulose; valves each with prominent midvein and 2 conspicuous marginal veins, usually glabrous, rarely pubescent; replum rounded; septum complete; style subclavate [clavate, conical, cylindrical]; stigma capitate (lobes not decurrent). Seeds plump, not winged, oblong [ovoid]; seed coat (reticulate or papillate), not mucilaginous when wetted; cotyledons incumbent. x = 7.
Annual, biennial or perennial medium-sized to tall herbs, with a taproot and usually erect ± branched stems, glabrous or with usually simple hairs. Racemes terminal, ebracteate, ± corymbose, with rather small flowers, in fruit cylindrical and elongate, usually rather lax. Sepals somewhat spreading, not saccate, often hooded, Petals nearly always yellow, obovate to spathulate. Stamens 6, with linear filaments; anthers oblong. Nectaries ± surrounding the lateral stamens and usually as strands outside each pair of median ones. Ovary cylindrical, with a short style and usually bifid stigma; ovules few to numerous. Fruit a siliqua, dehiscent (though sometimes tardily), linear to narrowly conical, and often very long; valves usually 3-nerved. Seeds uniseriate or rarely biseriate, ± oblong, without prominent testa sculpture, not mucilaginous.
Annual or perennial taprooted herbs. Hairs simple or 0. Stems erect or decumbent, leafy. Lvs pinnatifid or pinnate, often with large hastate terminal and deflexed lateral lobes; upper stem lvs sometimes not lobed. Racemes bracteate or ebracteate. Sepals erecto-patent, not saccate. Petals yellow, sometimes white. Stamens 6, without appendages. Lateral nectaries 4, median 2, often all joined into a ring. Style short; stigma capitate or weakly 2-lobed. Silique narrow-lanceolate to linear, dehiscent; valves usually with prominent midrib and 2 weaker lateral veins; beak 0 or very short, seedless. Seeds ovoid to oblong, not winged, in 1 row per locule.
Sep obtuse, ascending; pet small, yellow, obovate to spatulate, gradually narrowed to the claw; glands of the short stamens usually annular; filaments slender; anthers oblong; ovary cylindric; style short, scarcely differentiated; stigma capitate; ovules numerous; frs elongate, linear or subulate, terete or slightly quadrangular, tipped with the minute, persistent style; valves 3-nerved, with conspicuous midnerve and thinner lateral nerves; seeds in one row, oblong, smooth or nearly so; ours annuals or winter-annuals, ± pubescent with simple hairs, at least the lower lvs deeply pinnatifid. 90, widespread.
Annual or biennial herbs; hairs simple or absent. Leaves variable in dissection and size, usually less than 20 cm long. Sepals equal. Petals clawed. Stamens 6. Stigma more or less bilobed. Siliqua dehiscent, not beaked; valves with 3 veins. Seeds in 1 row per locule, mucous. Cotyledons usually flat. Radicle incumbent.
Silique long and slender with convex valves each with a prominent midrib and usually 2 less prominent lateral nerves, not or scarcely beaked.
Annual, biennial or perennial herbs with simple hairs.
Flowers usually yellow in lax racemes.
Sepals not or only slightly saccate.
Leaves entire or pinnatifid.
Seeds 1-seriate, ovoid.
Petals 4, unguiculate.
Cotyledons incumbent.
Stamens 6.