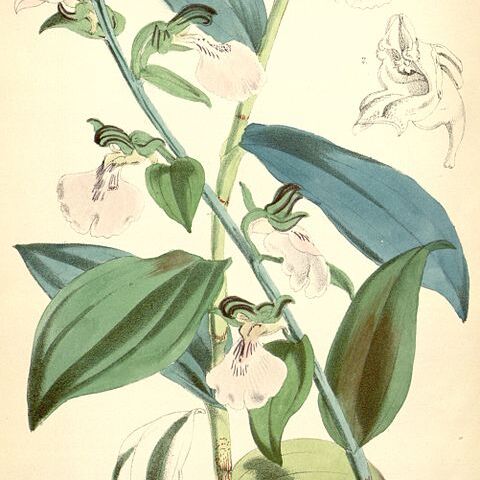
Terrestrial herbs up to 1 m. in height, with fusiform or ellipsoid tuberous roots. Stems usually leafy, the leaves often numerous and overlapping, usually lanceolate. Flowers few to numerous (up to 100), stalked, in a terminal inflorescence, white, yellow, pink or various shades of mauve or purple, often spotted darker; bracts leafy, the lower exceeding the flowers. Sepals free, the lateral ones spreading and oblique. Petals usually adnate at the base to the side of the column. Lip projecting forwards, rarely deflexed; basal part (hypochile) boat-shaped, sack-like or spurred; upper part (epichile) flattened, entire or 2–3-lobed. Column erect, rather slender; anther-loculi parallel, canals absent; caudicles of pollinia usually very short, viscidia naked; stigma hollowed out, rostellum middle lobe small, erect, folded, the side lobes often fleshy, surrounding the viscidia.
Basal part of lip (hypochile) spurred, saccate and boat-shaped; upper part (epichile) flattened, entire and 2–3-lobed, usually projecting forwards.
Flowers few to many in a terminal inflorescence, white, yellow, pink, mauve or purple often with darker spots.
Stigma hollowed out; rostellum mid-lobes small, erect, folded; side lobes fleshy, surrounding the viscidia.
Column erect, slender; anther loculi parallel, canals absent; caudicles usually short; viscidia naked.
Bracts leaf-like and longer than the flowers at least at the base of the inflorescence.
Terrestrial, rarely epiphytic, herb with fusiform or ellipsoid tuberous roots.
Petals usually adnate at the base to the side of the column.
Sepals free, the lateral sepals spreading and oblique.
Leaves often numerous and overlapping.
Stems leafy.