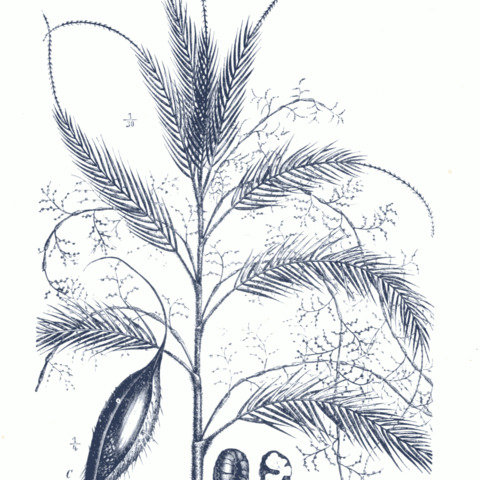
Stems clustered or less often solitary, mostly slender and climbing, occasionally non-climbing and then either short and subterranean or free standing. Leaves 10-60, pinnate, spiny; sheaths closed in climbing stems, open in non-climbers, variously hairy and spiny, hairs of young sheaths soon wearing off; sheath spines scattered or densely arranged (rarely absent), or arranged in rows, occasionally hairy on margins, variously shaped and colored, sometimes arranged in overlapping, interlocking rings and forming chambers; sheath apices usually extended above point of insertion of petiole into an inconspicuous or prominent ocrea; knees present in climbing stems; flagella present in climbers, whiplike and armed with small, grapnel-like spines; cirri present in few species (and then flagella absent, and vice versa); pinnae variously arranged and shaped, occasionally whitish or gray on abaxial surfaces. Plants dioecious. Inflorescences usually elongate, branched to 3 orders, male inflorescences more branched than female ones; branches and rachillae covered with overlapping bracts with clawed spines on outer surfaces in climbers; male flowers borne along opposite sides of rachillae; female flowers borne in pairs with a sterile male flower, along opposite sides of rachillae. Fruits mostly small, variously shaped and colored, usually 1-seeded, sometimes pedicellate, always covered with overlapping scales, these sometimes with a groove down middle; endosperm homogeneous or ruminate; germination adjacent; eophylls bifid or pinnate.
Solitary or clustering, pleonanthic, dioecious, spiny palms, mostly climbing but also erect or acaulescent (not in Australia). Stems slender; internodes short to long. Leaves paripinnate, occasionally terminating in a cirrus; leaf sheath tubular, usually armed, sometimes bearing a flagellum; petiole absent to long, usually armed; rachis usually armed. Pinnae evenly distributed or clustered, opposite or subopposite, variously armed; apices entire, rarely praemorse. Staminate and pistillate inflorescences superficially similar, axillary, basally adnate to adjacently distal internode and sheath of following leaf, compoundly branched, frequently flagellate at tip; bracts tubular, usually armed. Staminate flower solitary; stamens 6, epipetalous; pistillode small or lacking. Pistillate flower borne together with sterile staminate flower to form a dyad; staminodes 6; stigmas 3. Fruit ellipsoid-ovoid to globose, covered in vertical rows of imbricate scales. Seed subglobose, sarcotestal; embryo basal or lateral (not in Australia). Eophyll bifid or paripinnate (not in Australia).