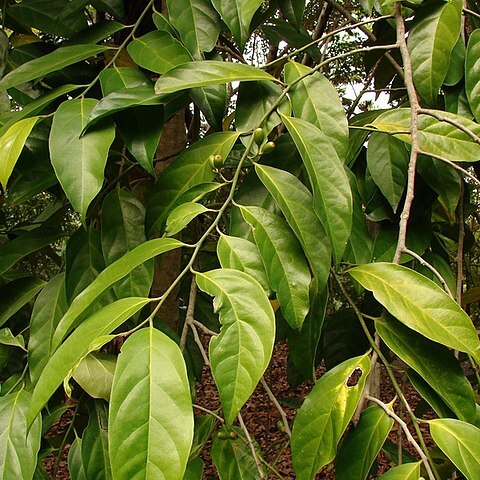
Dioecious trees, rarely shrubs. Branchlets usually slender, smooth, without lenticels. Leaves spirally arranged, entire, chartaceous to coriaceous, generally dark green above and paler beneath in fresh, often olivaceous or brownish, rarely blackish in dry specimens, often tubercled on the undersurface, generally pinnate-, exceptionally tripli-nerved, midrib and nerves often a little sunk above, reticulation generally absent; petiole often somewhat decurrent on branchlet, stoutish. Flowers functionally unisexual, articulate with the short, often distally thickened pedicel, in cymes loose to subcapitate, these 2-3(-4)-chotomously arranged on top of a peduncle, normally in the axils of leaves, rarely (also) opposite a leaf, or from defoliate branchlets, generally many-flowered in the ♂, few-flowered in the ♀ specimens; bracts small. Calyx cupular, minute, 4-5-toothed to almost entire, subpersistent. Petals 4 or 5 (rarely-7), valvate in bud, either remaining united below and forming a cup or distally dilated tube, or free to almost the base, tips inflexed, midrib on the inside rather obscure, caducous. Disk 0 or obscure. ♂ Flowers: Stamens 4 or 5 (rarely-7), free, often exserted; filaments thick, flattened, dilated upwards, apex attenuate, generally bearing shorter papillose or longer clavate hairs in front below the cells, or (also) on the back or connective; anther cells ovate-elliptic, basifixed, cells slightly or hardly divergent downwards. Rudiment of ovary conspicuous. ♀ Flowers: Calyx and petals as in the ♂ flowers, the petals sometimes absent. Staminodes present or absent; filaments linear, hairs shorter and less dense than in the ♂ flowers, cells reduced in size and void of pollen. Ovary cylindric; stigma large, thick-discoid, slightly 4-or 5-lobed or-crenate. Drupe ± oblongoid or ellipsoid, sometimes shortly attenuate (beaked) distally and slightly swollen (almost apophysate) and a little asymmetrical at base, crowned by the large persistent stigma; pericarp smooth, thin, fleshy or juicy; endocarp crustaceous or hard, smooth or generally with 8-10(-14) longitudinal ridges outstanding especially in the dry fruit. Seed 1; embryo minute in the top of the fleshy albumen.
More
Dioecious trees, rarely shrubs. Leaves alternate, occasionally distichous on lateral branches. Flowers functionally unisexual, in axillary, rarely leaf-opposed, cymes. Calyx cupular, shallowly 4-or 5-toothed. Petals 4 or 5, rarely to 7, valvate in bud, connate at base or united in a tube. Disc absent or obscure. Male flowers: stamens 4 or 5, rarely to 7, free; filaments flattened, hairy or papillose above, or glabrous; anthers latrorse to introrse, dorsifixed. Rudimentary ovary present. Female flowers: staminodes present or absent; filaments linear; anthers rudimentary. Ovary cylindrical; style obsolete; stigma discoid, 4-or 5-lobed. Fruit a 1-seeded drupe, ±ellipsoidal, crowned by persistent stigma; endocarp crustaceous or woody, smooth or with 8-15 longitudinal ridges.
Trees or shrubs. Leaves alternate, entire. Flowers small, unisexual (plants dioecious), in di-or trichotomous cymes, axillary, terminal, or opposite leaves; staminate cymes many flowered; pistillate cymes few flowered; bracts small. Sepals united in a 4-or 5-lobed cup. Petals 4 or 5, cohering in a short tube, valvate. Staminate flowers with stamens 4 or 5; filaments fleshy, clavate, 2 or 3 × as long as anthers, pilose, rarely glabrous, free from corolla tube. Disk pulvinate, coherent with ovary or reduced ovary. Pistillate flowers with stamens undeveloped or without pollen; disk often absent; ovary terete or obovoid; stigma capitate or discoid, sometimes 2-or 3-lobed, sessile. Drupe usually with persistent stigma at apex.
Primary and secondary forest, often as substage trees, both in lowland and in the montane zone up to c. 1800 m, occasionally also in mossy forest up to 2200 m (on Mt Kinabalu possibly higher), generally on clayey soil, very rarely limited to peat-swamp forest. Fl.fr. Jan.-Dec.