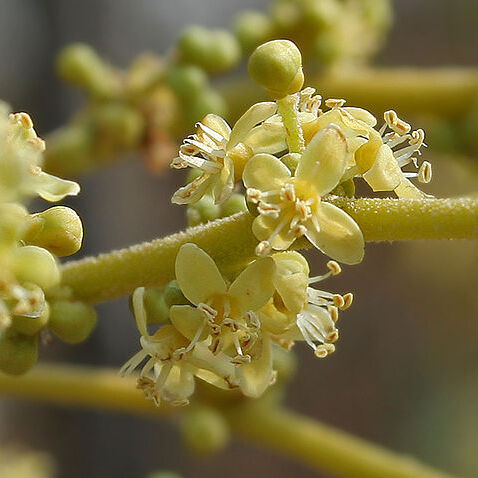
Trees, shrubs or undershrubs (extra-Mal.). Indumentum of stellate hairs. Leaves spiral, imparipinnate (rarely tri-or unifoliolate in extra-Mal. spp.), petioled. Inflorescences paniculate or ± spiciform, axillary or pseudo-terminal, appearing before (or at the same time in extra-Mal. spp. with) the leaves. Flowers unisexual (plants dioecious). Calyx 4-lobed. Petals 4, imbricate, glabrous. Stamens 8; filaments subulate, glabrous; anthers dorso-basifixed, ovoid, abortive and small in ♀. Disk intrastaminal, round, flat or concave. Ovary ovoid or oblong, 4-celled, usually 1 (or 2) fertile; styles 4, short; stigmas small, subglobose. Sterile pistil in ♂ small. Drupe 1-4-celled, usually 1-(or 2-)seeded; endocarp woody, with 1 (or 2) operculum (opercula). Seed with testa free from the endocarp; embryo straight, cotyledons free, plano-convex.
Trees, dioecious. Leaves imparipinnately compound; leaflets opposite, entire. Inflorescence a terminal panicle or raceme. Flowers 4-merous. Stamens 8; anthers ovoid, reduced and sterile in female flower. Disk intrastaminal. Ovary 4-locular, with 1 apical pendulous ovule per locule; styles 3 or 4, short; stigma subglobose; ovary in male flower rudimentary. Drupe small, subreniform, compressed; mesocarp thin; endocarp woody, 1-4-locular with operculum.
Female flowers: perianth similar to that of the male flowers; staminodes short; ovary ovoid or subglobose, 4-locular, with 2–3 abortive loculi; ovule pendent from a long funicle attached at the apex of the loculus; styles 3–4, subterminal; stigmas ± capitate.
Male flowers: calyx 4-partite, the segments imbricate; petals 4, imbricate; stamens 8 with the filaments subulate inserted below the disk; anthers ovate or sagittate, dorsifixed; disk ± cup-shaped, 8-crenulate with a 4-cleft vestigial ovary at the centre.
Drupe obovoid or ovoid, ± compressed or subglobose; mesocarp thin; endocarp woody, the surface unequally ridged and alveolate, with 1–2 ovate opercules at the apex.
Leaves alternate, imparipinnate or 3-foliolate or rarely 1-foliolate, usually clustered at the end of the branches; leaflets entire, sessile or petiolulate.
Panicles terminal or axillary, ± branched and pyramidal or spike-like (the lateral branches very short), often arising before the leaves.
Shrublets, suffrutices, shrubs or trees, with the young parts and inflorescences stellately tomentose.
Seeds ± reniform, compressed; cotyledons plano-convex.