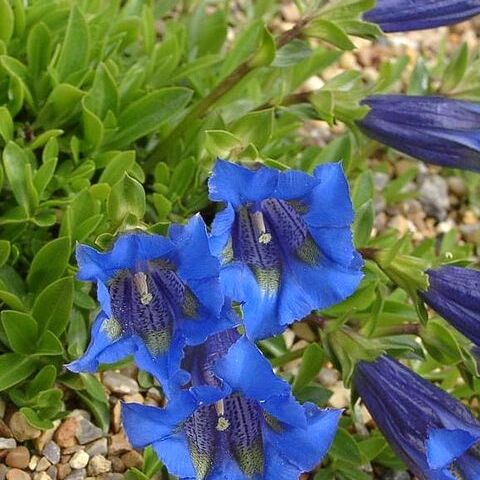
Herbs [shrubs or small trees], annual, biennial, or perennial. Stems ascending, erect, or twining. Leaves opposite, less often alternate or whorled, simple, base connate; stipules absent. Inflorescences simple or complex cymes, sometimes reduced to sessile clusters, often in a thyrse or 1-flowered. Flowers bisexual, rarely unisexual, 4 or 5 (or 6-8)[-12]-merous. Calyx tubular, obconic, campanulate, or rotate, lobes joined at least basally. Corolla tubular, obconic, salverform, funnelform, campanulate, or rotate, rarely with basal spurs; lobes overlapping to right or rarely valvate in bud; plicae (extensions of the corolla tube between the lobes) present or absent. Stamens inserted on corolla tube or occasionally at sinus between corolla lobes, alternate with lobes; anthers basifixed or dorsifixed, 2-locular. Nectaries absent or attached to ovary base or corolla. Ovary usually 1-locular at least apically, rarely 2-locular due to intrusion of a lamellate placenta into locular cavity. Fruit a 2-valved capsule, rarely a berry. Seeds many or rarely few, small; endosperm abundant [scant in saprophytic genera].
Herbs, rarely (non-Australian) saprophytes, vines, shrubs or small trees. Leaves opposite and decussate, or rarely (non-Australian) alternate, simple and entire, usually sessile, exstipulate. Inflorescence usually cymose or flowers solitary. Flowers usually actinomorphic, 4-or 5-(6–9)-merous, usually bisexual. Calyx tube short to elongate; lobes imbricate to valvate or open in bud, rarely absent. Corolla sympetalous; tube short to elongate; lobes contorted in bud, sometimes plicate in sinuses. Stamens usually perigynous, variously inserted in corolla tube, alternate with lobes, rarely some staminodal or obsolete; anthers bilocular. Nectaries often present, either as scales or pits on corolla tube, or as disc or glands surrounding base of ovary. Ovary superior, bicarpellate, 1-(or 2)-locular; ovules ±numerous; placentation parietal, axile or free-central; style simple or absent; stigma 1, entire or bifid, or stigmas 2, smooth or ±papillose. Gynophore sometimes present. Fruit a septicidal capsule or rarely (not in Australia) a berry. Seed with small, straight embryo embedded in oily endosperm.
Ovary superior, uni-or bilocular (through the intrusion of the cell walls), usually with many ovules in each cell, with parietal or, in the bilocular ovaries, axile placentation; style simple or rarely absent; stigma entire or bilobed or divided into 2 filiform branches (rarely stigmas deccurent along the sides of the ovary when style wanting)
Stamens as many as the corolla lobes, alternating with them, inserted on the corolla; filaments usually dilated at the base; anthers 2-thecous, with distinct parallel cells dehiscing lengthwise, sometimes twisted, or seldom with apical pores
Seeds usually numerous, subglobose, polyhedric to ovoid-ellipsoid, smooth, wrinkled, or reticulate-faveolate or sometimes frilled; testa crustaceous or membranous; embryo small, straight and elongate, embedded in the copious oily albumen
Corolla gamopetalous; tube campanulate, funnel-shaped or cylindric, sometimes with a constricted limb, 3–5(12)-lobed, usually contorted or rarely imbricate, often with scales or nectary-pits within the tube
Annual or perennial herbs, sometimes suffrutescent, rarely shrubs or small trees, erect to straggling, terrestrial or aquatic, rarely parasites or saprophytes, usually glabrous
Leaves simple, opposite (in the Flora Zambesiaca area), or seldom whorled, only rarely alternate, exstipulate, sometimes reduced and scale-like
Stamens the same number as the corolla-lobes and alternating with them, inserted on the corolla; anthers 2-celled, opening lengthwise
Ovary superior, mostly 1-celled with 2 parietal placentas, sometimes 2-celled with the placentas adnate to the septa; style simple
Inflorescence a terminal cyme, often paniculate, or axillary and fasciculate or, sometimes, reduced to solitary flowers
Flowers hermaphrodite or sometimes unisexual, actinomorphic or rarely zygomorphic, subsessile or pedicellate
Fruit usually capsular and dehiscent septicidally bivalved or rarely berry-like and splitting irregularly
Calyx tubular of (2)4–5, or rarely 6–12 sepals (lobes), imbricate (sometimes valvate)
Leaves opposite, often connate at the base; stipules absent
Flowers hermaphrodite, actinomorphic or rarely zygomorphic
Disk obsolete or annular or of 5 hypogynous glands
Calyx tubular or of separate sepals, imbricate
Seeds with copious endosperm and small embryo
Annual or perennial herbs
Fruit usually a capsule
Disk present or absent
Ovules often numerous
Corolla contorted