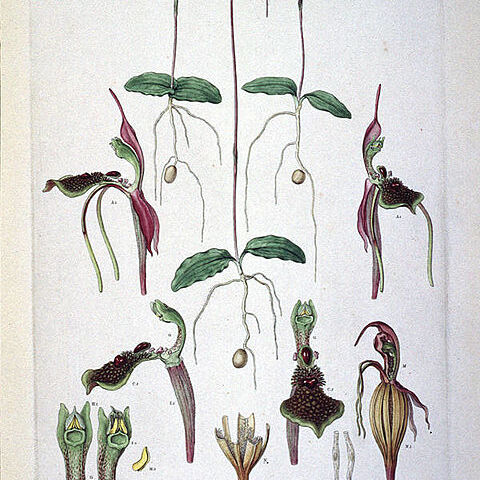
Fl. solitary or occ. 2; floral bract attached some distance below ovary, the intervening portion of stem elongating as fr. ripens. Per. glab.; dorsal sepal uppermost, erect or incurved, narrowed to base; lateral sepals and petals narrower, sts strongly deflexed. Labellum ± clawed, undivided; margins entire; calli prominent, variously shaped and arranged. Column elongate, erect to slightly curved, winged, with short column-foot; anther terminal, apiculate, papillose, pollinia 2 per cell, pollen finely granular; stigma prominent, discoid; rostellum small, median. Plants terrestrial, us. glab.; tubers ovoid, us. produced at some distance from parent plant. Lvs 2 (floral bract occ. foliaceous), basal, ± oblong. Genus of 6–7 spp., all found in eastern Australia.