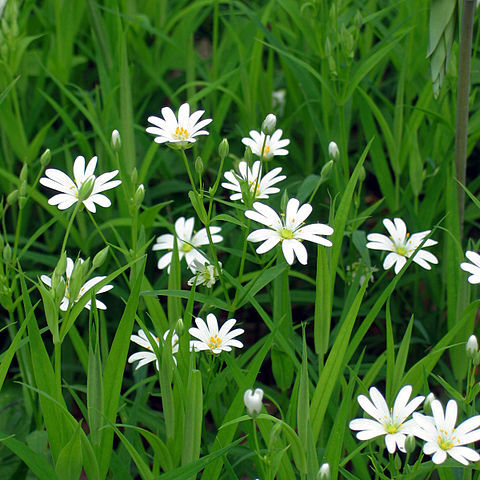
Annual or perennial herbs, often much branched and clambering, the stems somewhat resilient and occasionally suffruticose below. Leaves opposite, petiolate or sessile and somewhat perfoliate, exstipulate, in Central America rather broad and membranaceous. Flowers in few-flowered dichasial cymes or less frequently solitary in the axils of slightly reduced leaves. Sepals 4-5, not connate. Petals 4-5, rarely absent, white, deeply 2-cleft. Stamens 4-10; anthers versatile, 2-celled, the flattened hypogynous filaments connate below forming a brief glandular disk. Ovary superior, carpels 2-4, with as many filiform styles free to the base; ovules 4-many, camnpylotropous on basal, central or free central placentae. Capsule deeply or shallowly dehiscing into as many 2-cleft or rarely entire valves as there are styles; seeds 4-many, cochleate, smooth or tuberculate, estrophiolate, the embryo curved about the perisperm.
Herbs annual, biennial, or perennial. Roots or rhizomes filiform and slender, roots sometimes robust, fleshy. Stems erect, ascending, or prostrate. Leaves compressed, variously shaped, rarely needlelike; stipules absent. Flowers terminal, seldom only axillary, in cymes or solitary, small; bracts immediately subtending calyx absent. Sepals (4 or)5. Petals (4 or)5, white, rarely green, usually 2-cleft nearly to base, rarely retuse or multilobed, sometimes absent. Stamens 2--5 or (6--)10. Ovary 1-loculed, rarely 3-loculed when young; ovules numerous, rarely several and only 1 or 2 mature; styles (2 or)3(or 4). Capsule orbicular or ovoid, opening by valves (1 or)2 × number of styles. Seeds (1 to) numerous, reniform, slightly compressed, tuberculate or smooth; embryo curved.
Small, annual or perennial herbs. Stems slender, often thickened at nodes, glabrous or hairy. Leaves exstipulate, sessile or petioled, glabrous or pubescent with simple or stellate hairs. Inflorescences in lax, dichotomous cymes. Flowers hypogynous or slightly perigynous. Sepals (4 or) 5, free, herbaceous, usually 3-nerved. Petals (4 or) 5, rarely ab-sent, white, usually bifid, almost to the base. Stamens (3-)5 or 10, rarely more or absent. Nectarial glands present in the form of a disc or separate glands between or inside the stamens. Ovary unilocular; styles 2 or 3. Fruit a capsule opening by 4-6 valves. Seeds mostly numerous, rarely few to 1, reniform or spherical, rugose or verrucose.
Herbs, annual or perennial, glabrous or sparsely hairy. Leaves opposite; stipules absent; floral leaves herbaceous to scarious. Flowers in spreading dichasia or partial monochasia, or solitary or 2-flowered, 5-merous, bisexual. Sepals 5, free, usually narrowly to broadly ovate. Petals usually 5, free, bifid, shorter to longer than sepals, in some taxa reduced or absent. Stamens 1–10. Staminodes 0–5. Ovary 1-celled; styles usually 3, free to base; placentation free-central. Fruit a conical capsule, splitting to middle or below, usually 6-valved (twice the number of styles). Seeds 2–many, subdiscoid to nautiloid to obloid; testa minutely to prominently tuberculate.
Annual or perennial herbs. Hairs usually sparse and eglandular, or 0. Lvs opposite, exstipulate, sessile or petiolate, glabrous or ciliate, linear, lanceolate, ovate or orbicular. Infl. a dichasium or reduced to 1-2 fls; bracts scarious to herbaceous; epicalyx 0. Sepals 5, free, not veined or (1)-3-veined. Petals white, divided almost to base, rarely 0. Stamens 10 or fewer. Styles 3. Fr. a capsule, usually ovoid, sometimes globose or cylindric, dehiscing by 6 teeth; carpophore 0. Seeds usually 4-10, ovoid, flattened, tuberculate or papillate, not winged.
Annual or perennial herbs, often with slender diffuse stems, glabrous or hairy. Leaves opposite, simple, entire, flat to (rarely) subulate, exstipulate. Inflorescences dichasial cymes which are terminal to the branches, rarely the flowers solitary. Sepals free, 4–5. Petals 4–5, more or less deeply bilobed, white, or occasionally absent. Stamens 5 + 5, or fewer by reduction. Styles generally 3 but sometimes 2, free. Capsule unilocular with 3 (or rarely 2) or 6 (rarely 4) valves. Seeds either numerous or 1–4.
Fls solitary in the forks of the stem, or in terminal cymes; sep 5; pet 5, bifid, often deeply so, or lacking; stamens mostly 10, sometimes fewer; styles mostly 3(4) but 5 in S. aquatica; ovules numerous; capsule ordinarily dehiscent by twice as many valves as there are styles, but in S. aquatica with 5 apically notched or shortly bifid valves; low annual or perennial herbs with mostly rather small, opposite, exstipulate lvs; × most commonly=13. (Alsine, Myosoton) 100+, widespread, esp. N. Temp.
Fls hermaphrodite, regular, solitary or in cymes. Sepals 4-5, free; petals white, 4-5, us. very deeply bifid, sts lacking; stamens 10 or fewer; ovary 1-celled, styles 3 (rarely 2 or 4-5), free to the base; capsule opening by twice as many teeth as there are styles. Slender annual to perennial herbs. Lvs opp., simple, entire, exstipulate. About 85 spp., cosmopolitan. The 6 spp. indigenous to N.Z. are all endemic. Several naturalized spp. are widespread weeds.
Leaves opposite, sessile or petiolate, simple, entire, flat or very rarely subulate, exstipulate.
Capsule usually more or less rounded, opening at the apex by 3 or 6 (rarely 2 or 4) valves.
Inflorescences of terminal dichasial cymes, rarely flowers solitary.
Annual or perennial herbs usually with slender diffuse stems.
Petals 4–5, white, deeply bilobed, or occasionally absent.
Seeds numerous or occasionally 1–4-, roundish-reniform.
Stamens 10 (5 + 5) or fewer by reduction.
Ovary 1-locular; styles (2) 3, free.
Sepals 4–5, free.