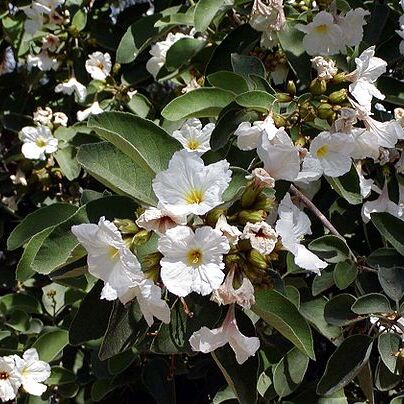
Medium sized trees, shrubs or woody climbers. Leaves alternate, rarely subopposite, stalked, unsually entire, sometimes indistinctly crenate. Inflorescences terminal or axillary, panicled to corymbose, sometimes very few-flowered, subglobose, with scorpioid branches. Flowers with a short, distinct pedicel or subsessile, (4-)5-16-merous, bisexual, sometimes functionally monosexual and dioecious. In male flowers the ovary reduced and style absent, in female flowers the anthers sterile. Calyx cup-shaped to campanu-late or tubular, lobes either irregular, 3-12, or regular, 5, or very short and reduced to a membranous, irregular margin, in some species growing with the mature fruit and becoming fleshy. Corolla hypocrateriform or funnel-shaped, large or small; lobes imbricate or nearly contorted in bud. Stamens of same number as corolla-lobes, included or exserted; filaments glabrous or pubescent at base; anthers oblong, ovate to subquadrate. Ovary 4-locular with one erect ovule in each locule; style twice forked, terminal; stigma elongate on each branch or subcapitate. Fruit drupaceous, as a rule partially included in the persistent, cupuliform calyx. Pollen grains 3-colpate, 3-colporate or 3-colporoidate, sexine tectate to semi-tectate, striate-reticulate or spiny and tuberculate in the Malesian species, 3-porate to pantoporate with semitectate, reticulate sexine bearing microtuber-cules in the exclusively American subgenus Varronia. Fig. 4.
Trees or shrubs, less often climbers or scramblers. Leaves alternate or in a few (but sometimes very common species) subopposite, petiolate, simple, often large, entire to crenate-dentate. Flowers mostly white, yellow or orange, hermaphrodite, polygamous or unisexual (plant dioecious), subsessile or pedicellate, borne in terminal or axillary dichotomous corymbs, panicles or subglobose clusters of cymes, the branches scorpioid, without bracts. Male flowers with 4–8 stamens, the filaments often hairy at the base; ovary rudimentary but style absent. Female with anthers sterile, otherwise similar to ♂ flowers. Calyx tubular or campanulate, smooth or with marked ribs, 2–5(–more)-lobed, persistent and accrescent in fruit. Corolla funnel-shaped or salver-shaped, mostly 5-but sometimes 3–8-lobed; tube short or long, cylindric or widened; lobes erect, spreading or reflexed, imbricate or subcontorted in bud.. Stamens exserted or included, the filaments glabrous or pubescent at the base. Ovary 4-locular with 1 erect ovule in each locule. Style terminal, twice bifid (or abnormally twice trifid), the ultimate stigmatic parts of the 4 branches linear to subfoliaceous or terminated by 1 capitate or peltate stigma, rarely with 4 separate styles. Fruits ovoid, globose or ellipsoid, included in or sitting in the persistent accrescent cupuliform calyx; endocarp bony with up to 4 locules but only 1–2 fertile. Seeds without endosperm.
Trees or shrubs. Leaves alternate, rarely opposite, usually evidently petiolate, margin entire or serrate, rarely lobed. Cymes mostly corymbose, ebracteate. Flowers bisexual, frequently heterostylous or ± functionally unisexual. Calyx tubular or campanulate, enlarged after anthesis, persistent. Corolla white, yellow, or orange-red, campanulate to funnelform, usually (4-or) 5(-8)-lobed; lobes antrorse or recurved. Stamens usually well developed; filaments often pubescent at base. Ovary 4-loculed, glabrous; ovule 1 per locule. Style twice 2-cleft, each branch with a spatulate or capitate stigma. Drupes ovoid, globose, or ellipsoid, frequently with watery or sticky fleshy mesocarp and bony endocarp, rarely with corky mesocarp or nutlike without fleshy mesocarp. Seeds 1-4, without endosperm; cotyledons plicate.
Trees or shrubs, glabrous or hairy. Leaves alternate or spirally arranged, petiolate. Inflorescence a few-flowered terminal or axillary cyme. Flowers sometimes heterostylous and sometimes functionally male by reduction of style and stigma. Calyx frequently cup-shaped; lobes short. Corolla small or large, white, yellow, orange or red. Stamens exserted or included. Style terminal, divided twice into 2 to give 4 branches, each with a stigma; stigmas capitate or clavate. Fruit a drupe with fleshy mesocarp or with a corky mesocarp and completely enclosed by persistent calyx, 1–4-seeded.
Corolla 4-5(7)-lobed, funnel-shaped to salver-shaped, white or yellowish; lobes imbricate or subcontorted in bud, shallow and obscure or oblong and conspicuous, patent or recurved at anthesis.
Ovary entire, 4-locular with 1 ovule in each locule (or reduced and abortive in male flowers); style terminal, twice cleft, with stigmatic branches linear or clavate.
Fruit drupaceous, partially or wholly surrounded by the enlarged persistent calyx; stone with 1-4 exalbuminous seeds, cotyledons plicate.
Stamens or staminodes inserted in the corolla tube, as many as the corolla lobes and alternate with them; anthers oblong.
Cymes arranged in lax or dense or sometimes very contracted and subglobose panicles, ebracteate, terminal or axillary.
Calyx tubular or ± campanulate, sometimes sulcate, usually splitting irregularly, 3-5-toothed, enlarging in fruit.
Flowers hermaphrodite or unisexual, actinomorphic, pedicelled or subsessile, the pedicels joined.
Leaves alternate, rarely subopposite, petiolate, entire to coarsely toothed.
Trees or shrubs sometimes dioecious.