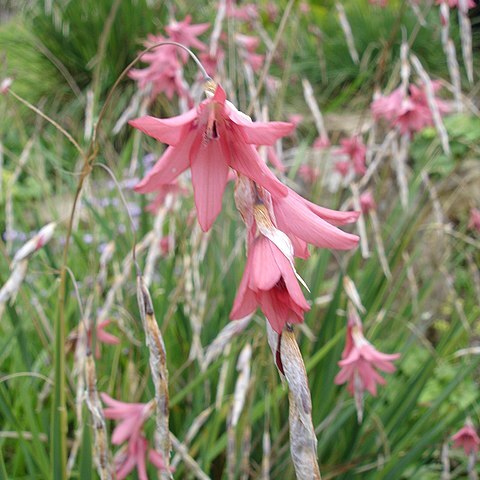
Tufted, evergreen perennial herbs. Corm depressed-globose; tunic fibrous. Leaves several, basal, linear, flat, tough, fibrous. Scape tall, slender, arching, with several pendulous, wiry branches; bracts small, scarious. Spikes lax, pendulous, few-flowered. Bracts scarious, straw-coloured with brown streaks. Flowers pendulous, actinomorphic, campanulate. Perianth tube straight, funnel-shaped; lobes equal, erect. Stamens equilateral, erect; anthers included, linear, sagittate. Style included, filiform, the 3 branches short, entire, recurved. Capsules ovoid to globose. Seeds few, globose, shiny.
Evergreen perennial. Corm with dry coats of parallel fibres. Leaves linear, rigid, grass-like, distichous. Panicle lax with slender pendulous branches. Flowers showy, each within 2 membranous spathe-valves; tube short, dilated at throat; lobes subequal, > tube. Stamens symmetrical. Style with 3 short, entire, cuneate branches. Capsule small, oblong. Seeds small, globose or angled by pressure. Spp. c. 25, of tropical and S. Africa. Adventive sp. 1.
Inflorescence consisting of spikes in a lax panicle; spikes few to many, erect or pendulous, terminal on the main axis and at the ends of wiry lateral branches of the flowering shoot; floral bracts ± solid, or scarious, and often translucent, lacerate above and usually brown-streaked or veined.
Flowers usually pink (also red, purple, yellow or white in southern Africa), actinomorphic, usually pendent and campanulate, with a fairly short campanulate perianth tube; tepals subequal; stamens, and often the style, included.
Leaves several, the lower 2–3 sheathing the stem base (cataphylls), these often dry and becoming fibrous; the foliage leaves linear, plane, with many strong parallel fibro-vascular veins, often without a midrib.
Evergreen perennial herbs with large corms, aerial parts persisting for several years; corms with coarsely fibrous tunics.
Style exserted from the perianth tube, seldom exceeding the tepal lobes; style branches simple, short, filiform.
Seeds globose or lightly angled, hard, smooth and often shiny.
Stem terete, slender and wiry, usually branched.
Stamens symmetrically disposed.
Capsules globose, coriaceous.