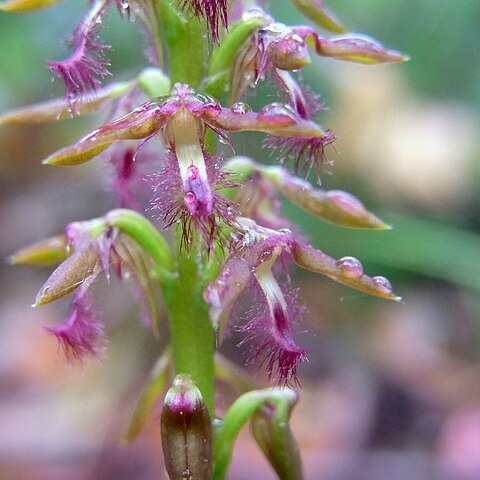
Plants growing singly or in loose groups. Root system consists of paired tubers (a parent tuber and a replacement tuber) and a few short roots, including 1 or 2 specialised mycorrhizal roots which tend to grow upwards (apogeotrophic). Leaf single, thin, wiry, solid. In flowering plants the leaf and peduncle of the inflorescence are inseparably fused and emerge from the soil as a single unit with an immature inflorescence at the apex, the leaf with a short, free apical part (free part) which may embrace the peduncle or spread away from the flower stem. Inflorescence racemose or spicate, few-to multi-flowered. Floral buds enlarge as the fused leaf/peduncle elongates, opening when mature. Flowers non-resupinate, sessile to subsessile, dull-coloured or dark, often with a fruity fragrance. Tepals glabrous, hairy or glandular-hairy. Dorsal sepal free, broader than lateral sepals, hooding column, sometimes with an apical gland. Lateral sepals free, narrower and longer than dorsal sepal, often basally gibbous, sometimes with an apical gland (often dropping off or reduced to vestigial remnants). Petals free, smaller than sepals, often longitudinally striped. Labellum hinged by small, flexible claw to apex of column foot, sometimes hinged delicately and labellum tremulous, vibrating in the slightest breeze. Labellum lamina unlobed, thin or fleshy, margins entire, serrulate, glandular or hairy. Callus a thin to fleshy, nectar-bearing plate, sometimes dominating the labellum, centrally grooved, surface smooth, papillate or colluviate. Column small with lobed wings and a well-developed basal foot. Pollinia 4, in two unequal pairs, clavate, sectile, yellow, attached via hamulus to viscidium.
More
Terrestrial orchids with single, perennial, rhizomatous rootstock (stem tuber) that increases in size annually, without roots. Leaf and base of inflorescence (peduncle) inseparably fused together, carrying the inflorescence at the apex of the flower stem. On emergence from ground, the fused peduncle/leaf structure lengthens, the immature inflorescence develops and the buds expand until anthesis. Inflorescence short, spicate or subspicate, few-flowered. Flowers small, non-resupinate, dull coloured, sessile to subsessile. Dorsal sepal free, concave, hooding column. Lateral sepals free, much longer than other tepals. Petals small, partially enclosed by dorsal sepal. Labellum firmly attached by its base to apex of column foot, remaining flexible. Callus a short raised plate, bilobed (no nectar). Column short, with basal foot. Pollinia 2, coarsely sectile, attached to viscidium by short, stout hamulus.
These orchids grow in freely draining to moisture-retentive soils in open forest, woodland, coastal scrub, heathland, rock outcrops and swamps. A preferred habitat is moss pads in shallow soil over rock plates.
More
Heathy and shrubby forests.