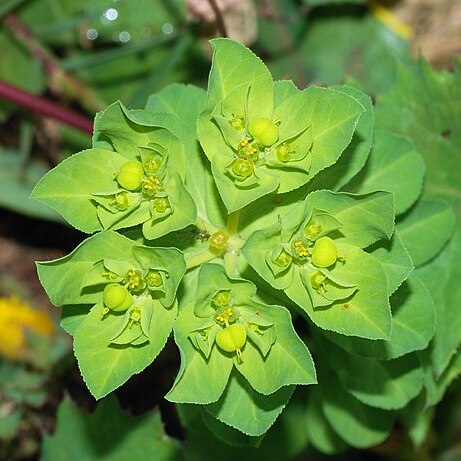
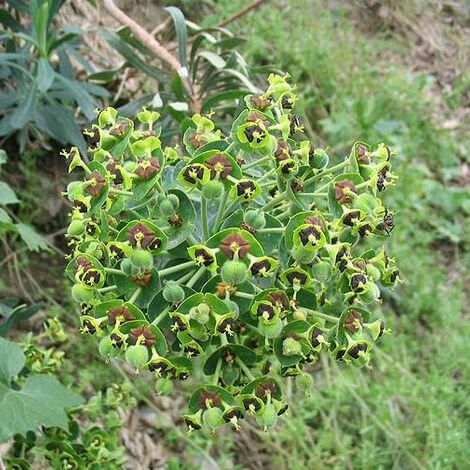
Herbs, subshrubs, or shrubs [trees, cactoid succulents, geophytes, vines], annual, biennial, or perennial, monoecious [dioecious]; hairs unbranched or absent; latex white. Leaves persistent, deciduous, or small and caducous proximally, alternate, opposite, or whorled, sometimes bractlike and subtending floral structures, simple; stipules absent or present, persistent or deciduous; petiole absent or present, glands absent; blade unlobed, margins entire, crenulate, crenate-dentate, or serrulate, laminar glands absent; venation palmate, palmate at base and pinnate distally, or pinnate, often only midvein prominent. Inflorescences bisexual [unisexual], terminal or axillary, pseudanthia (each consisting of cuplike involucre bearing glands on rim, these sometimes with petaloid appendages, enclosing solitary pistillate flower surrounded by (0–)1–80 staminate flowers, entire structure termed the cyathium), in monochasia, dichasia, pleiochasia, cymose clusters, capitate glomerules, or solitary; glands subtending each bract 0. Pedicels present. Staminate flowers: sepals 0; petals 0; nectary absent; stamen 1; pistillode absent. Pistillate flowers: sepals 0 (ovary subtended by a calyxlike structure in E. floridana, E. inundata, E. mesembrianthemifolia, E. porteriana, E. rosescens, and E. telephioides); petals 0; nectary absent; pistil 3-carpellate; styles 3, distinct or connate basally to most of length, unbranched or 2-fid. Fruits capsules, tardily dehiscent and with spongy mesocarp in E. lathyris [drupes]. Seeds globose to ovoid, oblong, cylindric, deltoid, pyramidal, or bottle-shaped; caruncle present or absent. x = 6, 7, 8, 9, 10.
Annual, biennial or perennial herbs, shrubs or trees, sometimes succulent and unarmed or spiny, with a milky usually caustic latex, monoecious (elsewhere rarely dioecious). Roots fibrous, or thick and fleshy, sometimes tuberous. Leaves opposite, alternate orverticillate, often stipulate, subtended by spiny outgrowths on some succulent species. Inflorescence with cyathia in simple, dichotomous or umbellate terminal or axillary cymes; bracts paired, often leaf-like, sometimes brightly coloured and showy. Involucres with (1-)4–5(–8) glands around the rim alternating with 5 fringed lobes. Male flowers in 5 groups separated by fringed membranes, bracteolate. Female flower subsessile or with the pedicel usually elongating and reflexed in fruit but straightening before dehiscence; perianth reduced to a rim below the ovary, seldom 3-lobed; ovary 3-locular, with 1 pendulous ovule in each locule; styles 3, partly united. Fruit a capsule, sometimes fleshy but becoming woody at maturity, loculicidally and septicidally dehiscent (a regma). Seeds with or without a caruncle.
Usually monoecious, rarely dioecious annual or perennial herbs, shrubs or trees, sometimes succulent, with milky sap. Lvs present or O, stipulate or not, alternate or opposite, usually entire or serrate, rarely lobed. Cyathia solitary, clustered or umbellate; umbels or clusters axillary or terminal, simple or compound and often forming many times compound dichasia; rays and cyathia usually subtended by lvs. Fls lacking a perianth, grouped in cyathia consisting of a cup-shaped involucre with usually 4-5 petal-like glands; glands serrate, entire, or with 2 horns; cyathium usually with several ♂ fls each consisting of a single stamen jointed to a pedicel and often separated from each other by small bracteoles, and a single usually longer-pedicellate (rarely sessile) ♀ fl.; ovary usually 3-celled with a single ovule in each cell; styles usually 3, often 2-fid at tips. Fr. usually a 3-celled capsule separating at maturity from the persistent axis; seeds smooth or variously sculptured.
Herbs, shrubs or trees, sometimes succulent, milky latex in all parts; monoecious or rarely dioecious. Leaves opposite, whorled or alternate, often serially on the same plant, simple; sometimes caducous particularly in succulent forms; usually petiolate except in succulents; stipules present or absent, sometimes glandular. Inflorescence a cyathium, the 5 cup-like lobes alternating at their tips with 4-5 glands, these with or without appendages. Staminate flowers in 4-5 cymes, the sub-tending bracteoles partly fused to the involucre or reduced or absent; naked; monandrous; pollen grains subglobose, reticulate to tectate, 3-colporate, sometimes operculate. Pistillate flo'wers terminal, solitary; perianth of 3-6 united sepals or absent; ovary 3-celled each with a single ovule, the styles 3, free or joined basally, usually partly bifid. Fruit. capsular (rarely drupaceous); seed ? ovoid, angled or terete, the surface smooth or variously sculptured, with or without caruncle.
Monoec. herbs with milky acrid sap. Lvs us. alt., stipulate. Fls nude, in compound cymes, subumbellately arranged, grouped within a cyathium; the small teeth alternating with conspicuous glands. ♂ ∞, of solitary stamens; ♀ a pedicelled 3-celled ovary; styles 3, stigmas often bifid; ovules 1 per cell. Fr. a 3-valved capsule. Subcosmopolitan genus of about 2000 spp., as us. understood. The N.Z. sp. also occurs in Norfolk Id.
Female flower subsessile or with the pedicel elongating and reflexed in fruit but straightening before dehiscence; perianth reduced to a rim below the ovary, rarely 3-lobed; styles partly united.
Herbs, shrubs or trees, sometimes succulent and unarmed or spiny, with a milky usually caustic latex, monoecious, rarely dioecious.
Inflorescence with cyathia in simple, dichotomous or umbellate terminal or axillary cymes; bracts paired, often leaf-like.
Leaves opposite, alternate or verticillate, often stipulate, subtended by spiny outgrowths in some succulent species.
Involucres with (1)4–5(8) nectiferous glands around the rim alternating with 5 fringed lobes.
Male flowers bracteolate, in 5 groups separated by fringed membranes.
Capsule sometimes fleshy but becoming woody at maturity, dehiscent.
Roots fibrous, or thick and fleshy, sometimes tuberous.
Seeds with or without a caruncle.